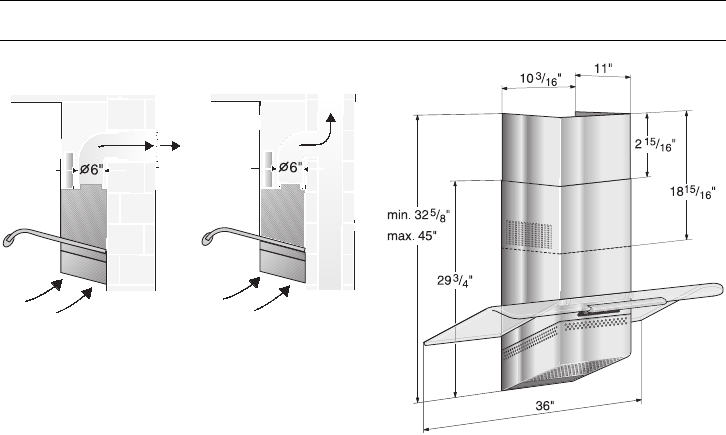
5
The exhaust air is discharged upwards
through a duct or directly through the
outside wall into the open.
D
Exhaust air should neither be directed
into a smoke or exhaust flue that is currently
used for other purposes, nor into a duct
that is used for ventilating rooms in which
stoves or fireplaces are also located.
Exhaust air may be discharged in
accordance with official and statutory
regulations only (e.g. national building
regulations).
Local authority regulations must be
observed when discharging air into smoke
or exhaust flues that are not otherwise in
use.
D
When the hood is operated in
exhaust-air mode simultaneously with a
different burner which also makes use of
the same chimney (such as gas, oil or
coal-fired heaters, continuous-flow heaters,
hot-water boilers) care must be taken to
ensure that there is an adequate supply
of fresh air which will be needed by the
burner for combustion.
Safe operation is possible provided that the
underpressure in the room where the burner
is installed does not exceed 4 Pa (0.04
mbar).
This can be achieved if combustion air can
flow through non-lockable openings, e.g. in
doors, windows and via the air-intake/
exhaust-air wall box.
If the air intake is inadequate, there is a
risk of poisoning from combustion gases
which are drawn back into the room.
ṇ WARNING – Avoid risk of poisoning – If
the air intake to the room is inadequate,
there is a risk of poisoning from combustion
gases which can be drawn back into the
room.
Note: When assessing the overall
requirement, the combined ventilation
system for the entire household must be
taken into consideration. This rule does not
apply to the use of cooking appliances,
such as hobs and ovens.
If the exhaust air is going to be
discharged into the open, a telescopic
wall box should be fitted into the
outside wall.
PRIOR TO INSTALLATION
Step 1: EXHAUST-AIR MODE