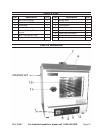
Page 6SKU 95887
For technical questions, please call 1-800-444-3353.
EXTENSION CORDS
As the distance from the supply outlet increases, you must use a heavier gauge extension
cord. Using extension cords with inadequately sized wire causes a serious drop in voltage,
resulting in loss of power and possible tool damage. (See Table A.)
The smaller the gauge number of the wire, the greater the capacity of the cord. For example,
a 14 gauge cord can carry a higher current than a 16 gauge cord.
(See Table A.)
When using more than one extension cord to make up the total length, make sure each
cord contains at least the minimum wire size required. (See Table A.)
Make sure your extension cord is properly wired and in good electrical condition. Always re-
place a damaged extension cord or have it repaired by a qualified electrician before use.
Protect your extension cords from sharp objects, excessive heat, and wet areas.
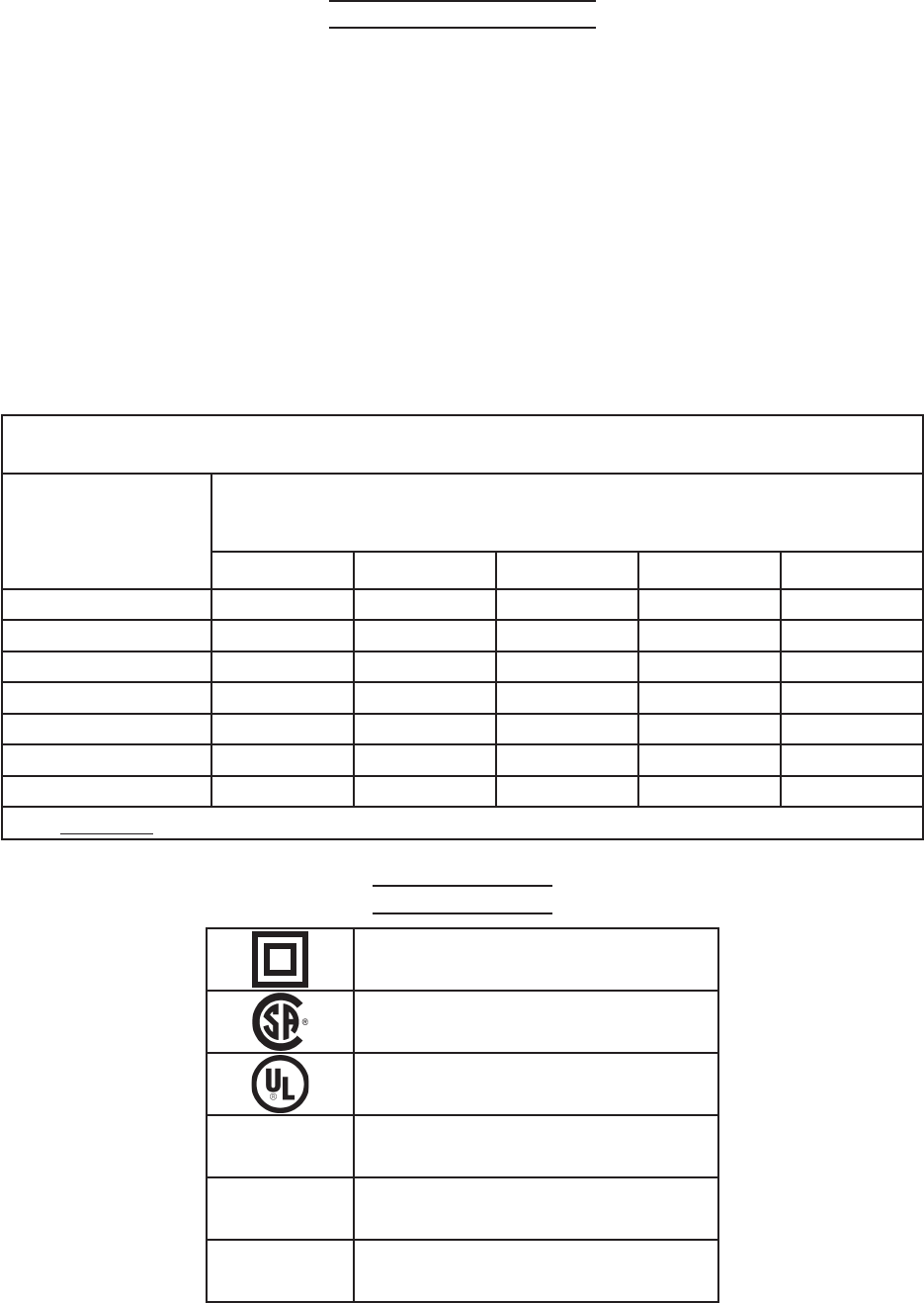
RECOMMENDED MINIMUM WIRE GAUGE FOR EXTENSION CORDS*
(120 OR 230 VOLT)
NAMEPLATE
AMPERES
(at full load)
EXTENSION CORD LENGTH
25 Feet 50 Feet 75 Feet 100 Feet 150 Feet
0 – 2.0 18 18 18 18 16
2.1 – 3.4 18 18 18 16 14
3.5 – 5.0 18 18 16 14 12
5.1 – 7.0 18 16 14 12 12
7.1 – 12.0 18 14 12 10 -
12.1 – 16.0 14 12 10 - -
16.1 – 20.0 12 10 - - -
TABLE A
* Based on limiting the line voltage drop to five volts at 150% of the rated amperes.
SYMBOLOGY
Double Insulated
Canadian Standards Association
Underwriters Laboratories, Inc.
V~
Volts Alternating Current
A
Amperes
n
0
xxxx/min.
No Load Revolutions per Minute (RPM)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.