Cookware
Aluminum: Medium-weight cookware is
recommended because it heats quickly
and evenly. Most foods brown evenly in an
aluminum skillet. Use saucepans with
tight-fitting lids for cooking with minimum
amounts of water.
Cast Iron: If heated slowly, most skillets will
give satisfactory results.
Enamelware: Under some conditions, the
enamel of some cookware may melt. Follow
cookware manufacturer’s recommendations
for cooking methods.
Glass: There are two types of glass cookware–
those for oven use only and those for surface
cooking (saucepans, coffee and teapots).
Glass conducts heat very slowly.
Heatproof Glass-Ceramic: Can be used for
either surface or oven cooking. It conducts
heat very slowly and cools very slowly. Check
cookware manufacturer’s directions to be sure
it can be used on gas cooktops.
Stainless Steel: This metal alone has poor
heating properties, and is usually combined
with copper, aluminum or other metals for
improved heat distribution. Combination metal
skillets generally work satisfactorily if they are
used at medium heat as the manufacturer
recommends.
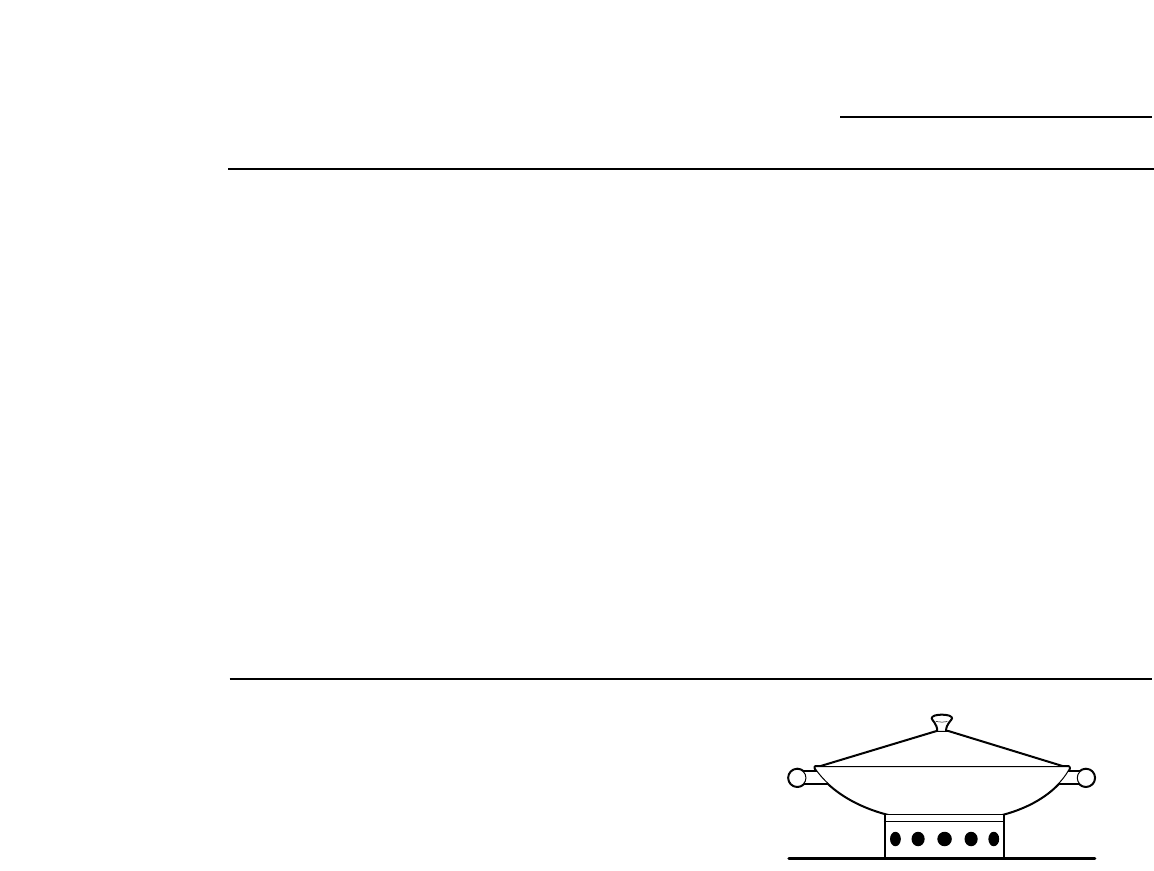
Wok cooking
Use woks with a support ring (provided on
some models) on the center burner only.
Make sure that the support ring is securely
locked onto the center grate fingers. Do not
try to use round bottomed woks without
a ring. You could be seriously burned if the
wok tipped over.
Use a 12″ or smaller diameter wok if the
cooktop is installed adjacent to standard wall
surfaces. If wall surfaces are constructed of
or covered with non-combustible materials
(such as masonry, ceramics, granite, stainless
steel, etc.) a larger diameter wok may be used.
Ensure that the wok is properly nested in the
ring prior to cooking. The wok should be
stable and the bottom of the wok should not
touch the center grate when in the wok ring.
12
Using Your Cooktop
Gas Cooktop