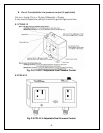
- 2 -
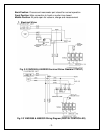
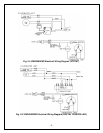
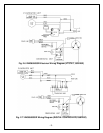
5. Pressure, Superheat and Subcooling Readings
NOTES: THE VALVES MUST BE IN THE MIDDLE POSITIONS TO READ
PROPERLY.
Complaint Possible Causes
a. High suction pressure and low head pressure
b. High suction pressure and low head pressure
Low superheat and low subcooling
c. High suction pressure and high head pressure
Low superheat and high subcooling
d. High to normal suction pressure and high head pressure
Low subcooling
e. High suction pressure and high head pressure
Low subcooling
f. High suction pressure and high head pressure
High superheat
g. Low suction pressure and low head pressure
High superheat and low subcooling
h. Low suction pressure and low to normal head pressure
High superheat and high subcooling
i. Low suction pressure and low head pressure
Low subcooling
j. Low suction pressure and low head pressure
Low superheat and low subcooling
k. Low suction pressure and low to normal head pressure
High superheat and normal to high subcooling
l. Low suction pressure and normal head pressure
High superheat and normal subcooling
m. Low suction pressure and high head pressure
High superheat and high subcooling
n. Low suction pressure and high head pressure
High superheat and high subcooling
o. low to normal suction pressure and high head pressure
High to normal superheat and high subcooling
a. Compressor may be bad
b. Expansion valve opened, too
much oil
c. Overcharge
d. Non-condensable gas
e. Air restricted, dirty condenser,
bad condenser fans
f. High room temperature, high
evaporator load
g. Undercharge
h. Liquid line restricted after
receiver, solenoid valve
restricted
i. Suction line restricted
j. Air restricted at evaporator,
evaporator iced
k. Evaporator restricted
l. Expansion valve restricted
m. Both evaporator and condenser
restricted
n. Liquid line restricted before
receiver
o. Condenser restricted
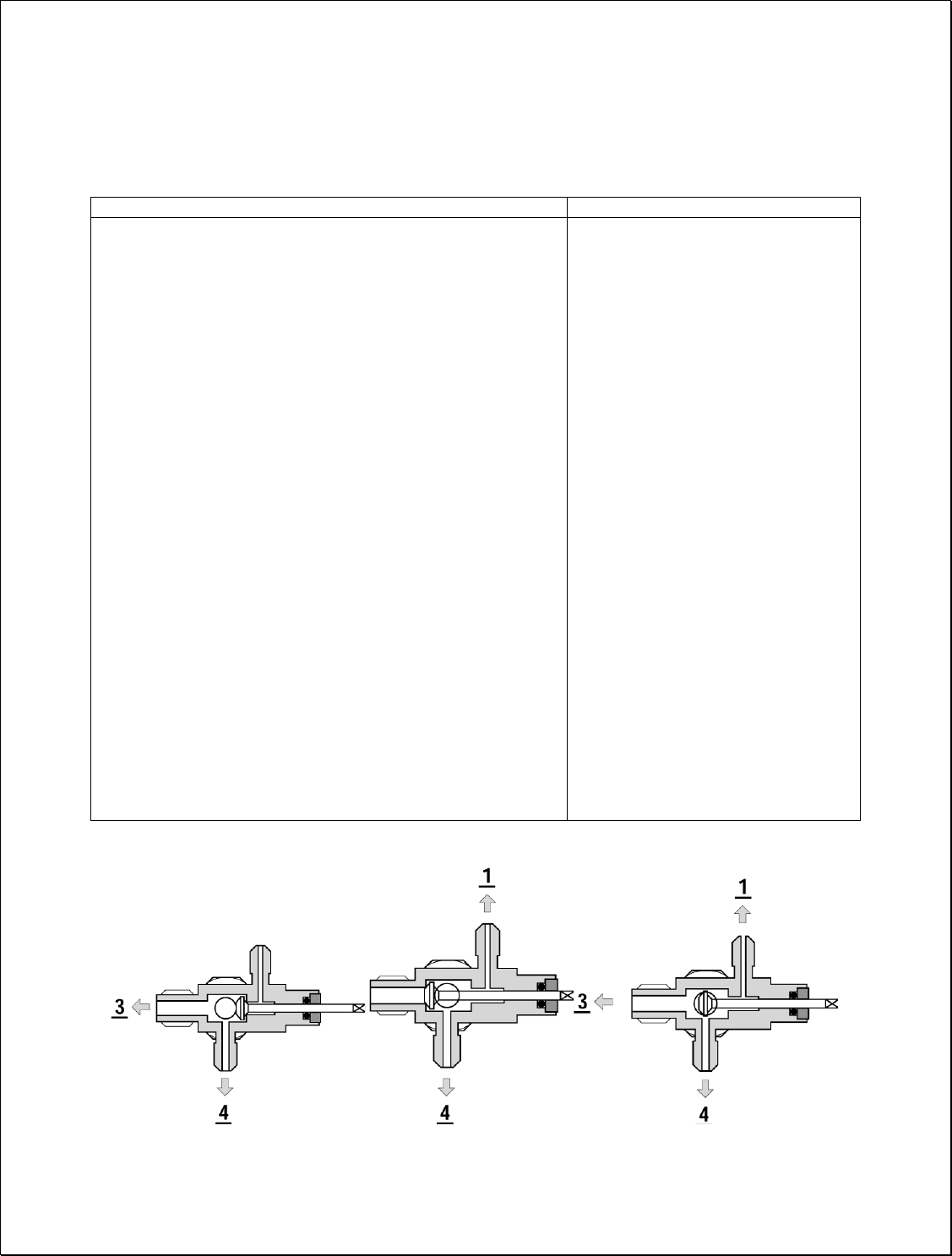
6. Valve Operation
SPINDLE BACK POSITION SPINDLE FRONT POSITION SPINDLE MIDDLE POSITION
Fig. 2.1 Valve Operation