Chapter 4 Timer Functions
63
8-bit Timer Operation (timers 2, 3)
4-2-2 Operation
■ Timer Operation (timers 2, 3)
Settings for timer operation are listed below. Timer 2 is used as an example.
(1) Set the TM2EN flag of the timer 2 mode register (TM2MD) to "0" to stop the count
operation of timer 2.
(2) Set the TM2CK2 0 flags of the TM2MD register to select fs, fs/4, fx, or
synchronized fx as the clock source.
(3) Set the TM2PWM flag of the TM2MD register to "0" so that normal timer operation
is selected.
(4) Set a value in compare register 2 (TM2OC).
(5) Set the TM2EN flag of the TM2MD register to "1" to start the timer.
(6) When timer 2 begins operation, binary counter 2 (TM2BC) will count upward from
X'00'.
(7) When the value of binary counter 2 matches that of the TM2OC register, the timer 2
interrupt request flag is set, and the binary counter 2 is reset to X'00' and begins to
count upward again.
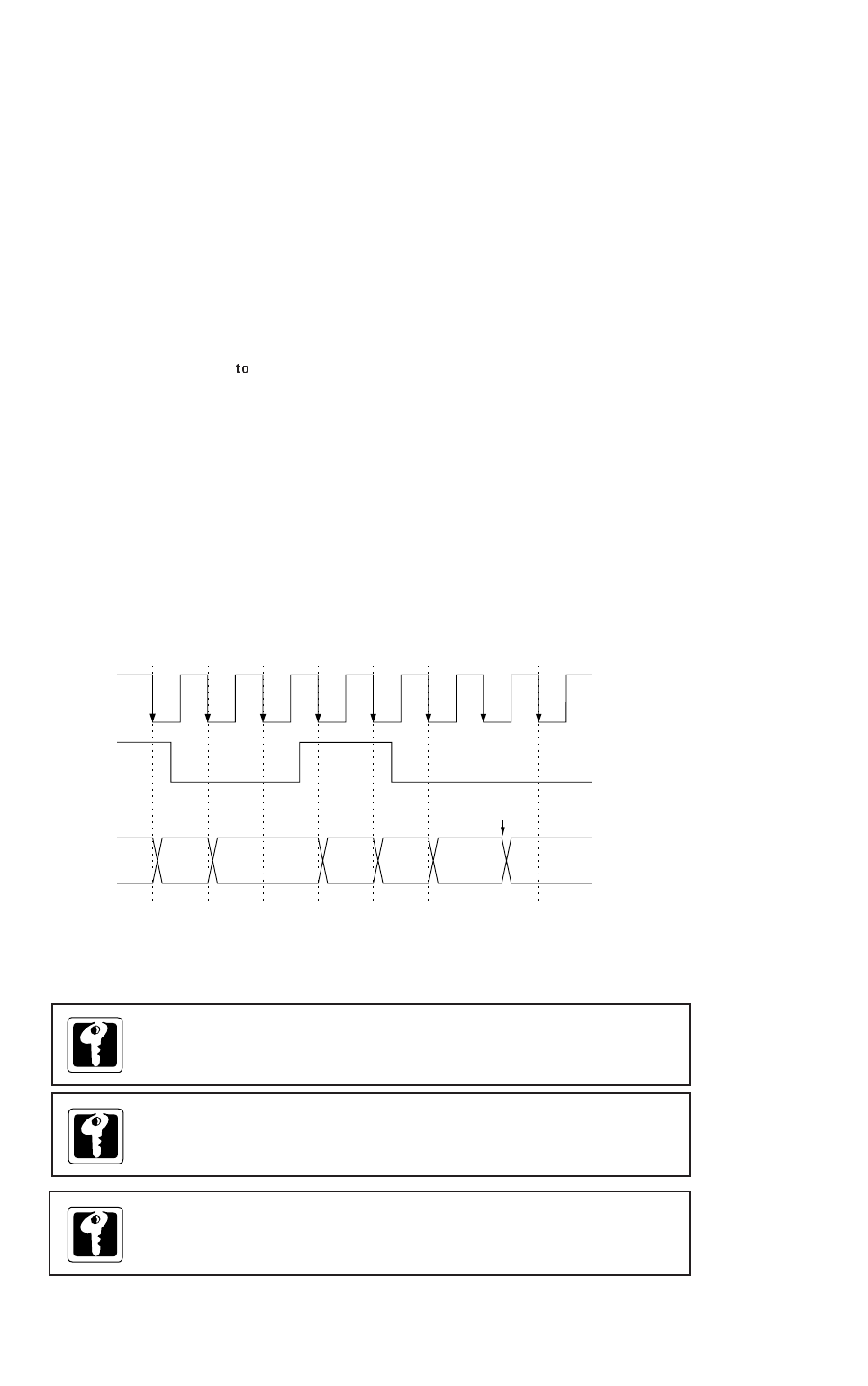
Figure 4-2-1 Binary Counter 2 (TM2BC) Count Timing
When servicing an interrupt, reset
the timer 2 interrupt request flag
before starting timer 2.
During a count operation, be
careful if the value set in TM2OC
is smaller than the value of binary
counter 2, since the count-up
operation will continue until
overflow occurs.
If fx is to be selected as the clock
source and the value of binary
counter 2 is to be read during
operation, select synchronized fx
in order to avoid reading data that
may be incomplete during count-
up transitions. However, with
synchronized fx, it is not possible
to return from STOP/HALT modes.
If the TM2EN flag of TM2MD register is changed simultaneously with
other bits, the switching operation may cause binary counter 2 to be
incremented.
If the value of TM2OC register is overwritten while timer 2 has
stopped counting, binary counter 2 will be reset to X'00' at the edge
of next count clock.
The value of TM3CK0~2 of T3MD register is unsettled. If timer2/
timer 3 is independently used, any mode except cascade
connection should be set.