12
Operating Manual -4048A digital signal processor
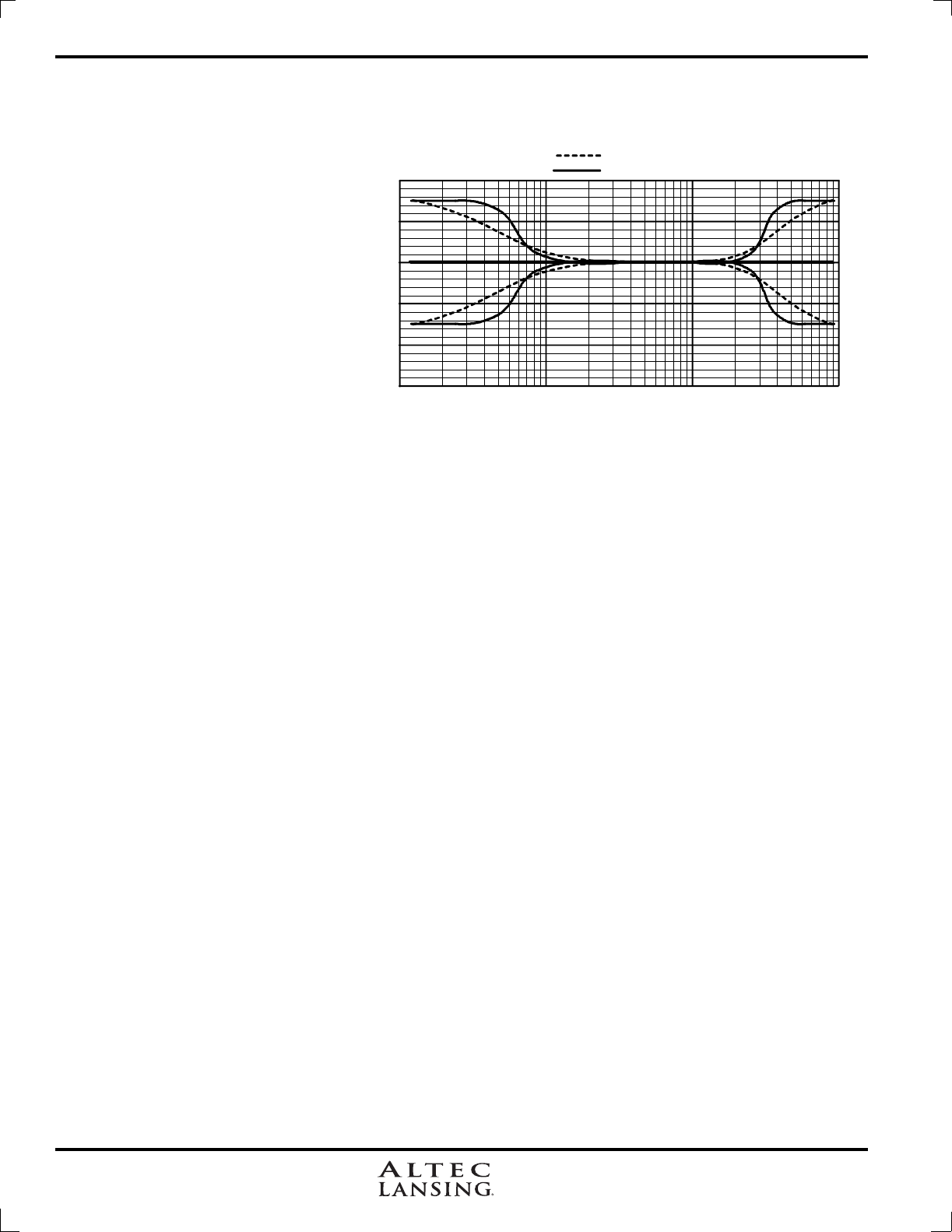
Shelving EQ filters: 1st order filters use a gentle 6dB per octave slope, while 2nd order filters use a 12dB per
octave slope for more a pronounced boost or cut. All shelving filters have a boost/cut range of +/-15dB. Low shelving
filters have a frequency range from 19.7Hz through 2kHz, and the high shelving filters range from 3.886kHz through
21.9kHz. Shelving filters are most useful as
broad tone controls to boost or cut the high
end or low end of an audio signal's frequency
content. Because they affect a wider spec-
trum of audio, they are not as suitable for
feedback control as parametric filters.
The EQ functions on all four inputs
and eight outputs are switched in or out on
an individual channel basis. In other words,
each input or output has one "switch" for all
of its EQ filters. If certain filters are not go-
ing to be used within a channel, simply leave
the gain for that filter at 0.0dB, and the filter
will have no effect.
All-Pass filters: The all-pass filter
type always has a flat frequency response but has a second-order phase response. The all-pass phase response is 0
degrees at low frequencies and -360 degrees at high frequencies and is -180 degrees at the center frequency selected.
7.3e Routing
Any of the four inputs can be equally routed, post input gain/EQ, to any or all of the eight output channels.
Click on the <Routing> box for a given input and select the desired outputs from the list of check boxes. Color coded
connect lines provide a visual image of the 4048A routing scheme.
7.3f HPF/LPF
Bandpass or crossover functions on the 4048A are available only on the eight output channels. Every channel's
crossover consists of a high pass filter (HPF) and a low pass filter (LPF), along with the frequencies and filter types
used. Each output's crossover section is essentially a bandpass filter, making it necessary for the user to map out ahead
of time which outputs will be used for the various frequency bands, and set the overlapping filter frequencies and types
accordingly. Note: The HPF determines the lower frequency limit of the signal, while the LPF determines the upper
frequency limit.
The frequency range for the high pass filter (HPF) is from 19.7Hz to 21.9kHz, with an option to turn the filter
off at the low end of the frequency selection. The low pass filter (LPF) offers the same frequency range, with the "off"
option at the high end of the frequency selection.
There are eight types of filters available in the crossover section, each suited to a specific preference or
purpose. The slope of each filter type is defined by the first characters in the filter type, 12dB, 18dB, or 24dB per
octave. The steeper the slope, the more abruptly the "edges" of the pass band will drop off. There is no best filter
slope for every application, so experiment to see which one sounds most pleasing in a specific system. The pre-loaded
presets all use 24dB/octave filters in the crossover section, but of course they can be changed to suit the application.
In addition to the frequency and slope, crossover filters can be selected as having Butterworth, Bessel, or
Linkwitz-Riley response. These refer to the shape of a filter's slope at the cut-off frequency, affecting the way two
adjacent pass bands interact at the crossover point. 24dB/octave Linkwitz-Riley filters produce a flat transition through
the crossover region, assuming both overlapping filters are set to the same frequency, slope, and response type. 24dB/
oct Linkwitz-Riley filters are the industry standard, the easiest to use, and the filter type recommended by Altec
Lansing. Other filter types are available, but may require polarity switching or other adjustments for proper results.
The following paragraphs offer a summary of the three filter types as used in the 4048A processor.
200Hz 2KHz 20KHz20Hz
0dB
-10dB
-20dB
+10dB
+20dB
-30dB
Low Shelf Hi
g
h Shelf
4048A Shelving Filters
2nd Order Filter
1st Order Filter


















