8
Selecting Surface Cooking Cookware
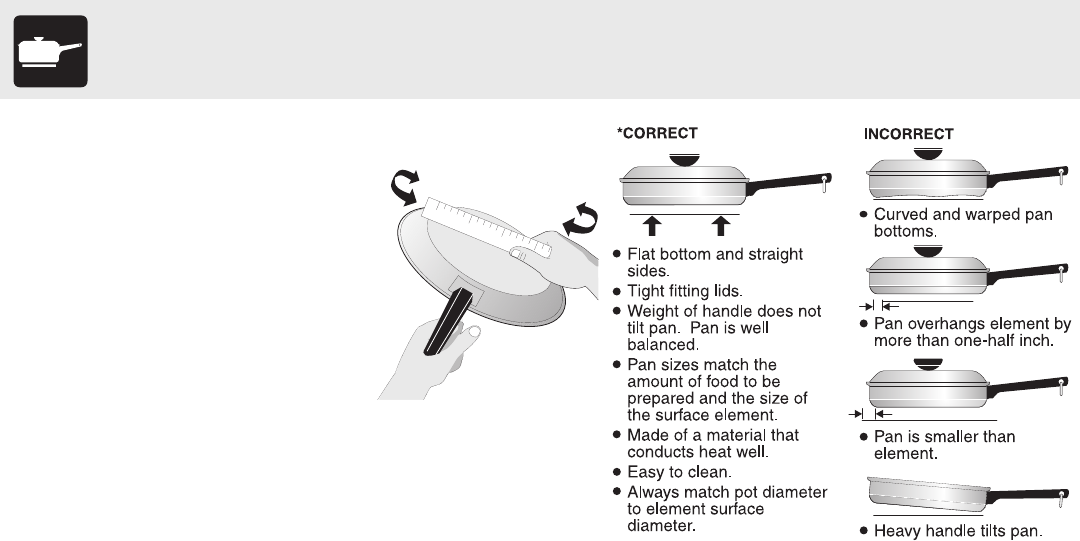
Figure 2
Cookware should have flat bottoms
that make good contact with the entire
surface heating element. Check for
flatness by rotating a ruler across the
bottom of the cookware (See Figure 1).
Be sure to follow the recommendations
for using cookware as shown in Figure
2.
Note: The size and type of cookware
used will influence the setting needed
for best cooking results.
Cookware Material types
The cookware material determines how evenly and quickly heat is transferred from the surface element to the pan bottom. The
most popular materials available are:
ALUMINUM - Excellent heat conductor. Some types of food will cause it to darken (Anodized aluminum cookware resists
staining & pitting). If aluminum pans slide across the ceramic glass cooktop, they may leave metal marks which will resemble
scratches. Remove these marks immediately.
COPPER - Excellent heat conductor but discolors easily. May leave metal marks on ceramic glass (see Aluminum above).
STAINLESS STEEL - Slow heat conductor with uneven cooking results. Is durable, easy to clean and resists staining.
CAST IRON - A poor heat conductor however will retain heat very well. Cooks evenly once cooking temperature is reached.
Not recommended for use on ceramic cooktops.
PORCELAIN-ENAMEL on METAL - Heating characteristics will vary depending on base material. Porcelain-enamel coating
must be smooth to avoid scratching ceramic cooktops.
GLASS - Slow heat conductor. Not recommended for ceramic cooktop surfaces because it may scratch the glass.
Surface cooking
Figure 1














