22
Proximity Hood
®
A. Exhaust
With all the filters in place, determine the total hood exhaust
volume with a rotating vane anemometer as follows:
1. All cooking equipment should be off. If the hood has internal
short circuit make-up air, it should be turned off.
2. Measuring Velocities
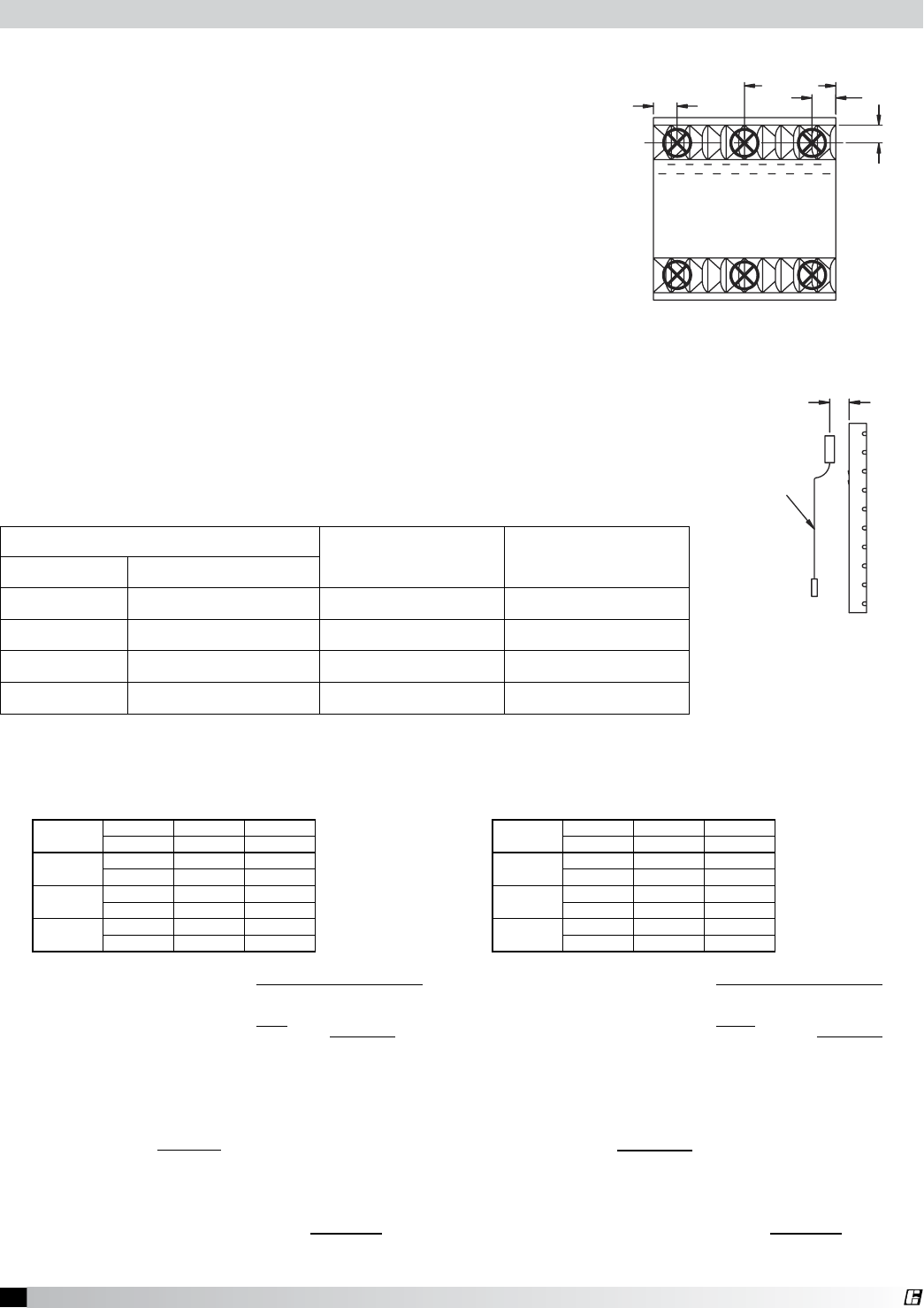
• Measurement should be taken at six locations per filter.
They must be over the inlet opening as shown in Fig. 31.
• Measure the velocity of each location. A digital 2.75 in.
(70 mm) rotating vane anemometer or its equivalent is
suggested. The center of the anemometer should be held
2 in. (50 mm) from the face of the filters as in Fig. 32. It is helpful to make brackets to keep the
anemometer at the 2 in. (50 mm) distance and parallel to the filter. Both squareness and distance
are important for accuracy.
3. Calculate the average velocity for the filter.
4. Determine the filter’s conversion factor from the table.
5. Calculate each filters volume in CFM by multiplying the average velocity
by the conversion factor.
2 in.
Rotating Vane
Anemometer
1/2 Width
1/4 Width
1/4 Width
1/2 Height
Fig. 32
Nominal Filter Size (H x L)
Imperial
Conversion Factor
Metric
Conversion Factor
Inches Millimeters
16 x 16 400 x 400
1.31 ft
2
.122 m
2
16 x 20 400 x 500
1.65 ft
2
.153 m
2
20 x 16 500 x 400
1.23 ft
2
.114 m
2
20 x 20 500 x 500
1.65 ft
2
.153 m
2
Grease-X-Tractor™ High Efficiency Filters or Grease Grabber™ Multi-Filtration System
2 in.
Rotating Vane
Anemometer
1/2 Width
1/4 Width
1/4 Width
1/2 Height
Fig. 31
Filter 1
225 201 187
210 238 197
Filter 2
228 222 226
237 240 220
Filter 3
230 245 240
250 223 219
Filter 4
225 265 219
245 221 200
Average slot velocity for Filter 1 =
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
=
1258
6
= 209.7 fpm
(repeat for each filter)
For a nominal filter size of 20 x 20, the conversion factor is 1.65
Volume for Filter 1 = Conversion Factor x Average Velocity
= 1.65 ft
2
x 209.7 ft./min.
= 346.0 cfm (repeat for each filter)
Example: (Imperial)
Hood Length = 7 feet 0 inches with four 20 x 20 filters.
Measure the velocities in fpm for each 20 x 20 filter
(six readings per filter)
Total hood volume
=
Filter 1
Volume
+
Filter 2
Volume
+
Filter 3
Volume
+
Filter 4
Volume
= 346.0 + 377.6 + 386.9 + 378.1 = 1488.6 cfm
Filter 1
4114.80 3675.88 3419.86
3840.48 4352.54 3602.74
Filter 2
4169.66 4059.94 4133.08
4334.26 4389.21 4023.36
Filter 3
4420.12 4480.56 4389.12
4572.00 4078.22 4005.07
Filter 4
4114.80 4846.52 4005.07
4480.56 4041.65 3657.60
Example: (Metric)
Hood Length = 2.13 meters, with four 500 x 500 mm filters.
Measure the velocities in m/hr for each 500 x 500 mm filter
(six readings per filter)
Average slot velocity for Filter 1 =
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
=
23006
6
= 3834 m/hr
(repeat for each filter)
For a nominal filter size of 500 x 500, the conversion factor is .153
Volume for Filter 1 = Conversion Factor x Average Velocity
= .153 m
2
x 3834 m/hr
= 586.7 m
3
/hr (repeat for each filter)
Total hood volume
=
Filter 1
Volume
+
Filter 2
Volume
+
Filter 3
Volume
+
Filter 4
Volume
= 587 + 642 + 657 + 642 = 2528 m
3
/hr