PAGE 24 — MQ62TDD TRASH PUMP • OPERATION AND PARTS MANUAL — REV. #0 (07/30/09)
SETUP
Before Starting
1. Read safety instructions at beginning of manual.
2. Place pump as near to water as possible, on a firm
flat, level surface.
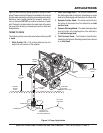
3. To prime pump, remove fill cap (Figure 4) and fill pump
case with water. If the pump case is not filled with water
before starting, it will not begin pumping.
4. Check for
leaks
between pump and engine. If water is
leaking between the pump and bearing housing, the
seal inside the pump may be worn or damaged.
Continued operation of the pump is not recommended.
Further usage of the pump under these conditions
may cause severe water damage to bearing housing
assembly.
Hoses, Clamps and Strainer
1. Check that all hoses are
securely
attached to the pump.
Make certain suction hose (Figure 4) does not have
any air leakage. Tighten hose clamps and couplings
as required.
2. It is recommended that 2 clamps be used when
securing the suction hose to the inlet side of the pump.
3. Remember suction hoses must be
rigid
enough not to
collapse when the pump is in operation.
4. Check that
the
discharge
hose (Figure 4) is not
restricted. Place hose so that it lays as straight as it
is possible on the ground. Remove any twists or sharp
bends from hose which may block the flow of water.
5. Make sure the
suction strainer
(Figure 4) is clean
and securely attached to the water end of the suction
hose. The strainer is designed to protect the pump by
preventing large objects from being pulled into the
pump. Failure to use a strainer could cause damage to
the pump, impeller, pump shaft, pump bearings, or wear
plate.
Pump casing must be filled with water before
using pump, otherwise pump will not be able
to begin pumping.
6. Shorter suction lift and suction hose length will produce
better performance.
7. The discharge hose is usually a
collapsible
(thin-
walled) hose, however if a thin-walled discharge hose
is not available, a rigid suction hose can be substituted
in its place.
8. Pipes, hoses, fittings and elbows all produce friction
that can significantly reduce the flow of water. Keep
hose length to a minimum and minimize the use of
elbows and other fittings to reduce friction.
9. Always use a suction hose or pipe that matches the
size of the pump inlet to insure optimum performance
and reduce the risk of damage to the pump.
10. It is recommended that the discharge hose or pipe
match the size of the pump outlet to reduce friction as
much as possible. Using a discharge line that is larger
than the pump outlet will reduce friction and improve
water flow. Similarly, a smaller line will reduce water
flow by increasing friction.
DANGER — High Pressure
PVC discharge hoses and thin-walled
rubber hoses can easily fail at the end of
the hose fittings. Leaks from the hoses can
cause high-pressure liquid to be
discharged, causing dangerous conditions.
Make sure pressure rating of hoses
exceeds the pump maximum pressure to
prevent hose failure.
CAUTION — Strainer Placement
The strainer should be positioned so it will remain
completely
under water
. Running the pump with the
strainer above water for long periods can damage the
pump.
CAUTION — Equipment Damage Hazards
DO NOT pump flammable fluids, corrosive chemicals
or fluids containing toxic substances. These fluids can
create potentially dangerous health and environmental
hazards. Contact local authorities for assistance.