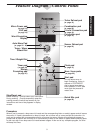
Before Operation
5
Microwaves and How They Work
Microwaves are a form of high frequency radio
waves similar to those used by a radio, including
AM, FM and CB.
Electricity is converted into microwave energy by the
magnetron tube (which is the heart of the microwave
oven).
From the magnetron tube, microwave energy is
transmitted to the oven cavity. The microwaves are
converted to heat in the food. The microwaves enter
from the outside of the food and travel through the
food. Continued cooking to the centre occurs by
conduction.
Although pacemakers used to be affected by
microwaves (as well as by other radio waves), they
are now shielded and are not bothered by these
interferences. This allows people with pacemakers
to sit calmly by their radio or television and cook
with microwave ovens.
When the microwaves come in contact with a
substance, any one or a combination of three things
may occur. They can be:
1. REFLECTED
2. TRANSMITTED
3. ABSORBED
Reflection
Metal substances REFLECT microwave energy
because there is no absorption and there is no
heating. This is why the oven interior is either
stainless steel or paint-coated steel. This ensures
that the microwaves are kept inside the cavity and
evenly distributed throughout the food with the help
of the turntable.
Transmission
Such substances as paper, glass and plastic
TRANSMIT microwave energy and do not become
hot except from food. Because these substances do
not reflect or absorb microwave energy, they are
ideal materials for microwave cooking containers.
Absorption
Food contains moisture and will ABSORB
microwave energy, which causes the moisture
molecules within the food to vibrate at an incredible
rate (2,450,000,000 times per second). Friction,
created by vibration, produces heat energy which is
conducted throughout the food.
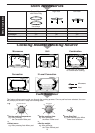
Cookware and Utensil Guide
It is important to use correct containers when
cooking in a microwave oven. The following will help
you to make the right selection.
How to Test a Container for Safe Microwave
Oven Use
Fill a 1-cup glass measure with water and place it in
the microwave oven along with the container to be
tested; heat one minute on HIGH. If the container is
microwave oven safe, it should remain comfortably
cool and the water should be hot. If the container
becomes very hot, it has absorbed some microwave
energy and should not be used. This test cannot be
used for plastic containers.
Paper Products and Freezer Wrap
Waxed paper, paper plates, cups and napkins
should not be used for heating or cooking food by
Convection, Combination and Grill. Freezer wrap
should not be used as it is not heat resistant and
may melt. Paper towels, greaseproof paper and
bake paper may be safely used for short periods of
time for covering or lining.
Glass, Ceramic and China
Heat-Resistant glass cookware is invaluable in
microwave cooking. Many of these items are readily
available in most homes: glass jugs, mixing bowls,
loaf dishes, covered casseroles, oblong baking
dishes, pie plates and round or square cake dishes.
Examples of this type of cookware are Pyrex® and
Corningware®.
Dinnerware can be used for microwave heating.
Many brands of dinnerware are microwave safe.
Check the care information for reference to
microwave use for dinnerware and serving pieces. If
dinnerware is marked ovenproof, it frequently is safe
to use in the microwave oven. However, to be sure,
check by conducting a microwave dish test.
Several types of glassware and dinnerware are
not recommended for use in the Microwave Oven.
Do not use dishes with metallic trim or containers
with metal parts. Do not use cups or mugs with
glued on handles, as they may fall off with continued
heating. Do not use delicate glassware. Although
the glassware may be transparent to microwave
energy the heat from the food may cause the
glassware to crack.