7.6.
Microwave Oven Use and Care Guide
How Your Microwave Oven Works
(Cont.)
The rate of heating depends on the moisture content, shape,
volume and amount of food present. Metallic materials totally
reflect microwaves. Non-metallic materials such as glass, paper and
plastics are partially transparent to microwaves. Microwaves do not
directly heat the oven walls and most cooking utensils because they
do not absorb microwave energy. However, they frequently get very
warm through being in direct contact with hot food.
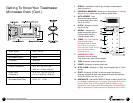
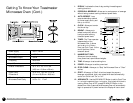
Materials to Avoid
in a Microwave Oven
Aluminum pan or tray
Food carton with
metal handle
Metal or metal-trimmed
utensils
Metal twist ties
Plastic foam
Wood
May cause arcing. Transfer food into
microwave-safe dish.
May cause arcing. Transfer food into
microwave-safe dish.
Metal shields the food from microwave
energy and may cause arcing.
May cause arcing and could cause a
fire in the oven.
Plastic foam may melt or contaminate
the liquid inside when exposed to high
temperature.
Wood will dry out and may split. Avoid
using wooden containers or utensils in
the oven.
Cooking
Accessories
(not included
with Microwave) Remarks
How Your Microwave Oven Works
The microwave oven has an electronic tube called a magnetron that
produces microwaves, very short radio waves. The microwaves then
pass through a wave-guide and into the oven cavity. The microwaves
penetrate the food and cause water molecules within the food to
vibrate extremely rapidly. This vibration causes considerable friction
or heat between the water molecules resulting in a rapid rise in
temperature. This type of heating is very efficient and the cooking
time is therefore shorter than in a conventional oven.