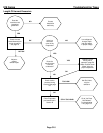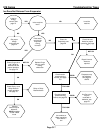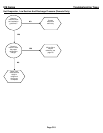
ICE Series Refrigeration System
Page E1
Refrigerant Cycle and
Components
Before diagnosing the refrigeration
system, it is very important that the
refrigerant charge be correct.
Whenever the refrigeration system
has been opened, the filter-drier
must be replaced and the proper
refrigerant charge must be weighed
in. See refrigerant charge data on
page A5–A8.
Refrigerant Pressures
The suction pressure at the
beginning of the freeze cycle can vary +/- 10 psi
(.7 bar) depending on operating conditions. Reference Chart on page E10-E13. Pressures less
than this may indicate an undercharge. The discharge pressure on water-cooled units should be
250 psi (17.01 bar) for R404a units and 150 psi (10.21 bar) for R134a units. The discharge
pressure on air cooled units will vary with ambient conditions but will typically run higher than water
cooled units. Remote condensers located in ambient temperatures below 70°F (21°C) will typically
run a lower discharge pressure. See Mixing Valve later in this section.
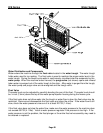
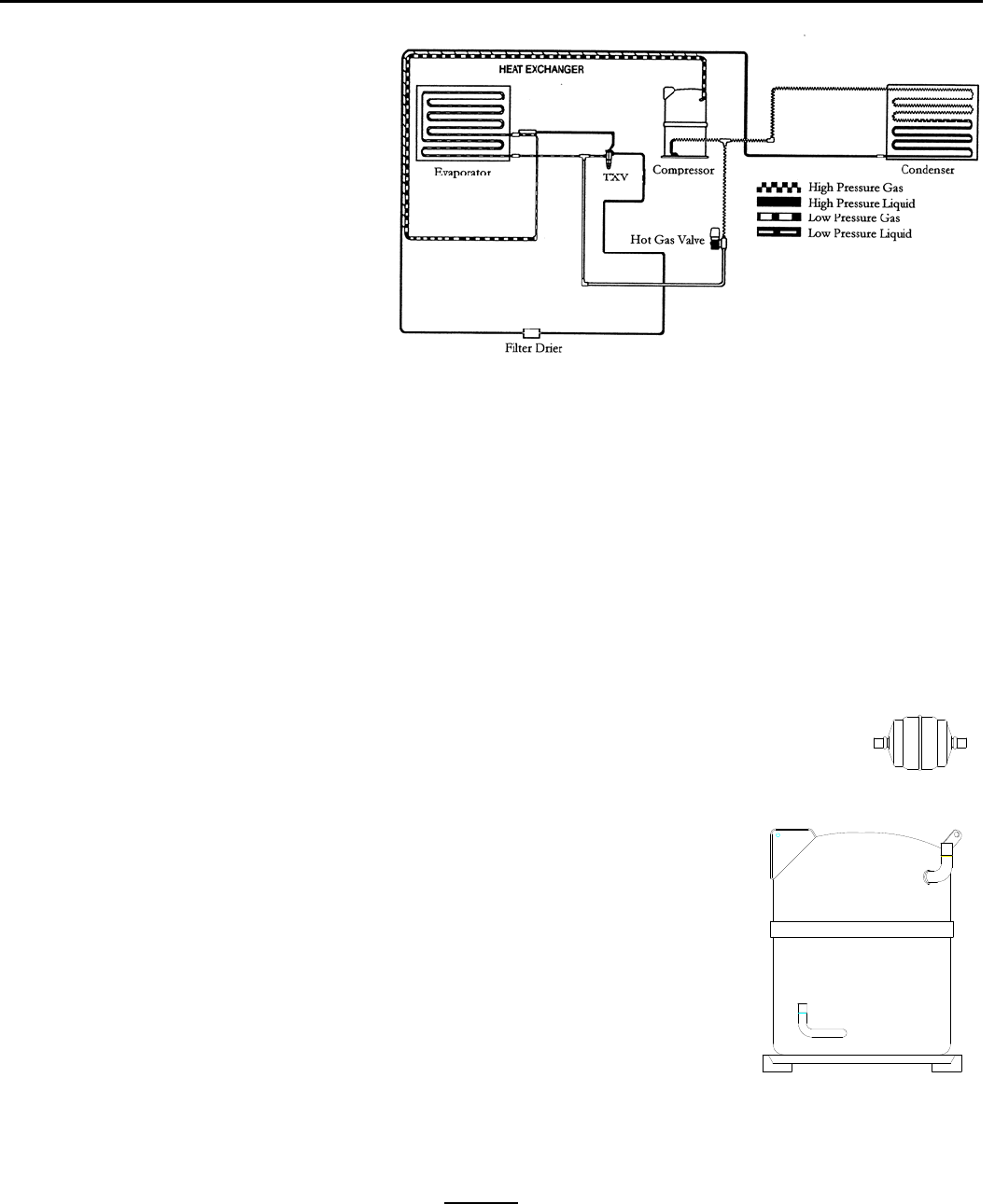
Refrigerant in a gas state is pumped throughout the refrigeration system by a hermetic
compressor to the condenser. Heat is removed from the refrigerant either by forced air
movement through an air-cooled condenser or transferring heat from the refrigerant to water
through a water-cooled condenser. The refrigerant changes to a liquid when cooled.
The refrigerant in a liquid state passes through a filter drier. The filter drier traps
small amounts of moisture and foreign particles from the system. The filter drier must
be replaced whenever the refrigeration system is opened or if the refrigerant charge
has been completely lost.
Compressor
The compressor runs during the entire cycle. If the valves in the
compressor are damaged, the compressor will be unable to pump
refrigerant efficiently. Damaged valves are usually the result of another
problem in the refrigeration system such as liquid refrigerant returning to
the compressor, oil slugging or high head pressure. When a compressor
is replaced it is important that the refrigerant charge be weighed in and
the system checked for proper operation to prevent a repeat failure.
An inefficient compressor will usually have a higher than normal suction
pressure at the end of the cycle. The freeze cycle will be longer than normal and/or the harvest
cycle may be excessively long. Check the compressor amperage draw 5 minutes into the freeze
cycle. If the compressor amp draw (Reference data plate on ice machine back panel) is less than
70% of rated full load amps, the compressor may be inefficient. These symptoms may also be
caused by other problems, therefore it is important to use the troubleshooting trees when
diagnosing a problem. See Electrical System for more information on the compressor and
compressor start components.