Page 24 IQ–AMB-5 / IQ–SMX-6
Reference Manual
AMB-5 / SMX-6 IQ Mixer/Multiplexer
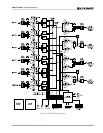
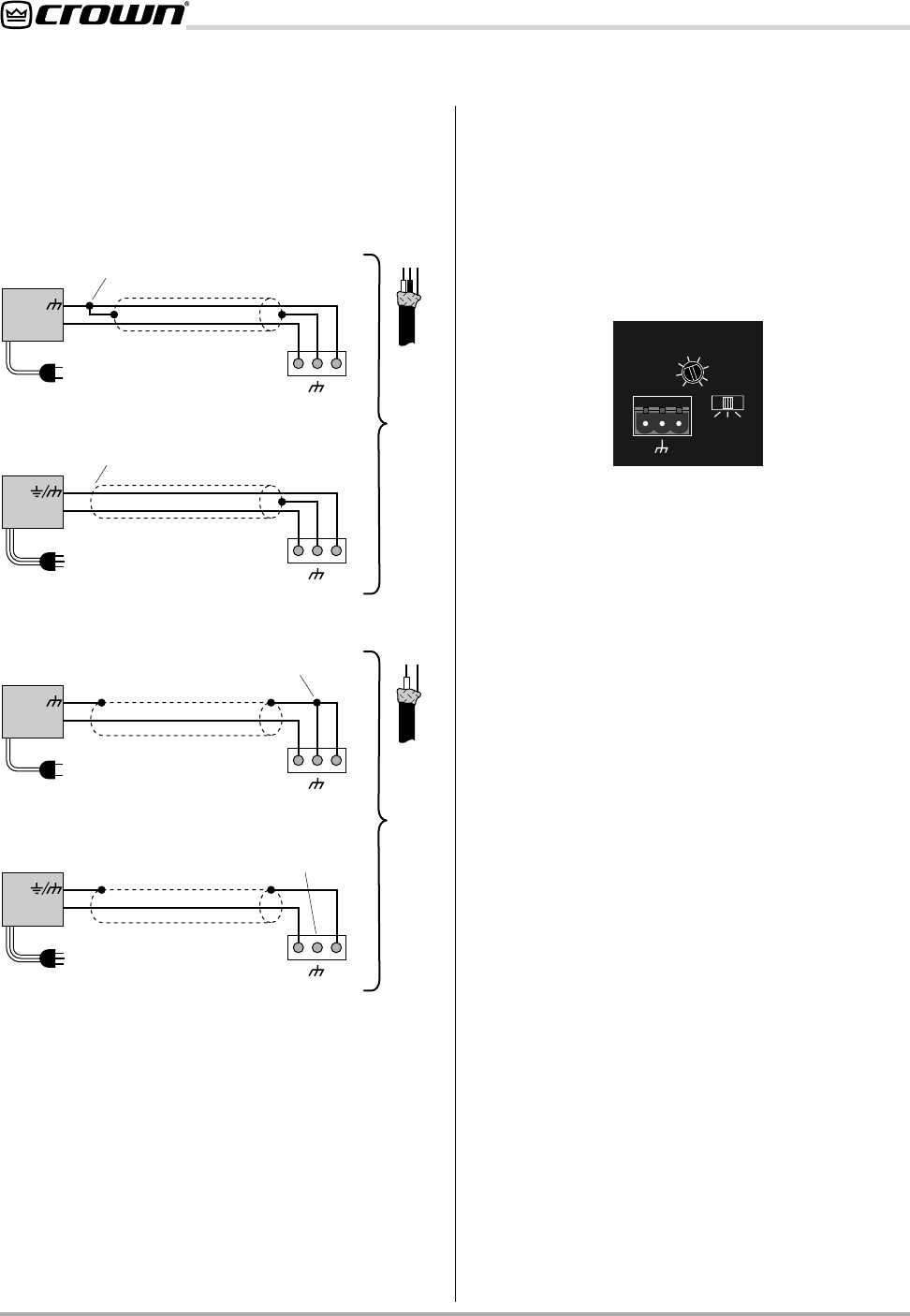
Balanced sources should be wired as shown in Figure
6.3. Notice that the shield is not connected to the
chassis ground of the source if the source is also
connected to the AC ground (that is, it has a grounded
AC plug). This prevents unwanted ground loops.
+
2-wire line cord
(or battery power)
Output
INPUT
Floating
source
3-wire grounded line cord
(or other ground connection)
Shield not connected
at this end
INPUT
Grounded
source
Twin-lead shielded cable
Shield connected
to ground terminal
+
Output
+
2-wire line cord
(or battery power)
Output
INPUT
Floating
source
3-wire grounded line cord
(or other ground connection)
Input ground
terminal not used
INPUT
Grounded
source
Single-conductor coax
or twisted pair
Shield connected to both negative
(–) and ground input terminals
+
Output
+–
+–
+–
+–
5 the paging level at a train station can be automati-
cally adjusted so pages can be heard over the roar of
an incoming train and yet quieted to an appropriate
level during periods of softer ambient sound levels.
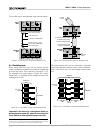
The sensing input section of the back panel is shown
in Figure 6.5 below. It has the same features as the
other mic/line inputs: input gain control and input level
switch.
+–
LMP
0
-5
-10
-12
5
10
15
21
ADD 25
FOR MIC
SENSE
IN
Figure 6.4 Unbalanced Audio Input Wiring
Figure 6.5 Sensing Input Section
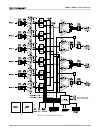
Unbalanced sources should be wired as shown in
Figure 6.4. The examples in Figure 6.4 are grouped
according to whether twin-lead shielded wire or single-
conductor coax (and twisted pair) wire is used.
6.1.2 IQ–AMB-5 Ambient Sensing Input
In addition to its automatic mixing capabilities, the IQ–
AMB-5 also has the ability to adjust the output level of
Channel 1 to the ambient sound level. (Remember,
Channel 2 functions manually only). It does this with its
sensing input (input 6). For instance, with an IQ–AMB-
The most common use of the sensing input is to con-
nect a microphone (such as a Crown
PZM
®
) and lo-
cate the microphone so that it can accurately receive
the ambient sound level. Great care must be taken in
the placement of the ambient sensing microphone so
that it is not too close to the loudspeakers being driven
by the system.
It is also possible to connect more than one ambient
sensing microphone to the sense input. This can be
accomplished by taking advantage of the manual mix-
ing function of Channel 2. Simply connect each ambi-
ent sensing microphone to one of the five regular
inputs of the IQ–AMB-5 and use the IQ software to
assign each of them to Channel 2 only. Switch the
sense input to the line-level position (L) and connect
the main audio output of Channel 2 to it. Use the IQ
software to control the level of the ambient sensing
microphones. The microphones which are located in
more critical areas can be set to a higher level so they
will trigger the level controller first.
Be sure the microphone has adequate sensitivity for
the spectral content of the ambient sound. For ex-
ample, a microphone with a bandwidth designed
solely for speech reinforcement may not have ad-
equate low-frequency sensitivity to pick up the low-
frequency noise of machinery in a factory.
6.1.3 Output
Three-terminal removable barrier block connectors are
provided for audio output (Figure 3.15). Both “main”
and “bus” outputs are provided for each of the two
mixer channels. They are balanced and can drive 1200
ohms or more to +26 dBu or 600 ohms to +20 dBu.