9
those microwave oven which have the power control function.
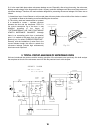
FIG.3-1 is the power control circuit diagram of brand microwave oven, WP700. This is a typical instance of
conduction ratio control. This oven adopt time and power controller as a whole. When a 120V, 60Hz alternating
current is inputted, the time and power motor is always at working condition. At the FIG.2-7, S5 is always
conducted. Made the S5 working 30 seconds as a circle, the conduct time can be successively adjusted from 5
seconds to 30 seconds. When power select switch is set at “HIGH”, S5 is always conducted, the output of the
microwave oven is 700W(full power) when the power select switch is set at defrost position, S5 would conduct for
14.4 seconds, and cut off for 15.5 seconds, and the average output of the oven is 336W.
2
2
.
.
4
4
.
.
3
3
T
T
H
H
E
E
R
R
M
M
A
A
L
L
C
C
U
U
T
T
O
O
U
U
T
T
Thermal cutout actually is a thermal sensor switch, usually, it is fixed on the shell of the magnetron, and series
connected with the primary circuit of the magnetron to control the power input. At normal condition, the thermal
cutout is always conducted (FIG.2-8). When something wrong with the cooling system that cause some abnormal
conditions, such as molding or thermal breakdown, which made the temperature of the magnetron reach the limit
value. Then, the thermal cutout would work to turn off the power to prevent the magnetron from being damaged.
2
2
.
.
4
4
.
.
4
4
H
H
E
E
A
A
T
T
I
I
N
N
G
G
C
C
H
H
A
A
M
M
B
B
E
E
R
R
Heating chamber is the place where the microwave and the food affect mutually. There are lots kinds of chamber.
Accord-ing to the working characters, it can be classified to carton type, cavity type, radiation type, slow type
(surface wave type), etc. The present adopt chamber for food cooking microwave oven is the typical carton type
heating. (FIG.2-8). The heating chamber is mainly composed of oven door and oven cavity. From the microwave
theory, it is a microwave resonant cavity that can contain many kinds of oscillating models simultaneously.
Microwave enters into the oven cavity through the wave guide and the coupling appliance, and most of its energy
is absorbed by the food after it is reflected in the cavity repeatedly, those which haven’t been absorbed will be
reflect to the magnetron. A good designed oven cavity should have a good impedance matching with the
magnetron, the energy should be less reflect, and distribute evenly in the oven cavity, improve the heating
efficiency. Generally, at the same input power, the larger the cavity, the less the energy density a unit volume
would have in the oven, and the more energy on the inside wall of the cavity would lose, thence, it would certainly
slow down the heating speed, low the heating efficiency. Moreover, too big of the cavity would either waste the
material or appears very heavy. The material for cavity usually use non - magnetic stainless steel or zinc - plating
steel, and have no high requirements for the conducting rate. The inside coating of the cavity requires beautiful in
look, durable when use (should be resistant against damp, heat, acid and alkali), it should also comply with the
food health requirements.
To improve the heating evenness there often fixed a turntable glass tray at the bottom of the cavity (FIG. 2-8). It is
through changing the relative place of the microwave and the heating matter to improve the heating evenness.
The turntable tray is usually made of heat – resistant glass, the glass contains some dielectric loss, it can,
somewhat, protect the magnetron when the cavity loading less.
There often fixed a dust – proof, low – loss and heat – resistant dielectric cover (such as mica sheet). Sometimes,
an impedance matching metal stick was fixed near the coupling or in the wave guide.
The door is designed for inspecting, taking and placing the heating food, it is also one side of the cavity (FIG .2 -
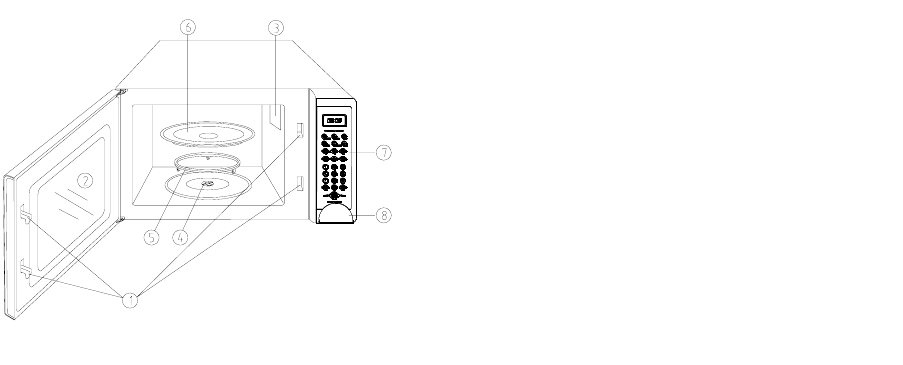
1. Safety interlock switch
2. Door window
3. Air vent
4. Roller Shaft
5. Turntable supporter
6. Glass tray
7. control panel
8. door release button