© Copyright 2012 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-712BR
31
4. To save changes, click Apply.
Open a device on your network to the Internet
This router can provide access to devices on your local area network to the Internet
using the Virtual Server, Special Application, method (DMZ NOT recommended).
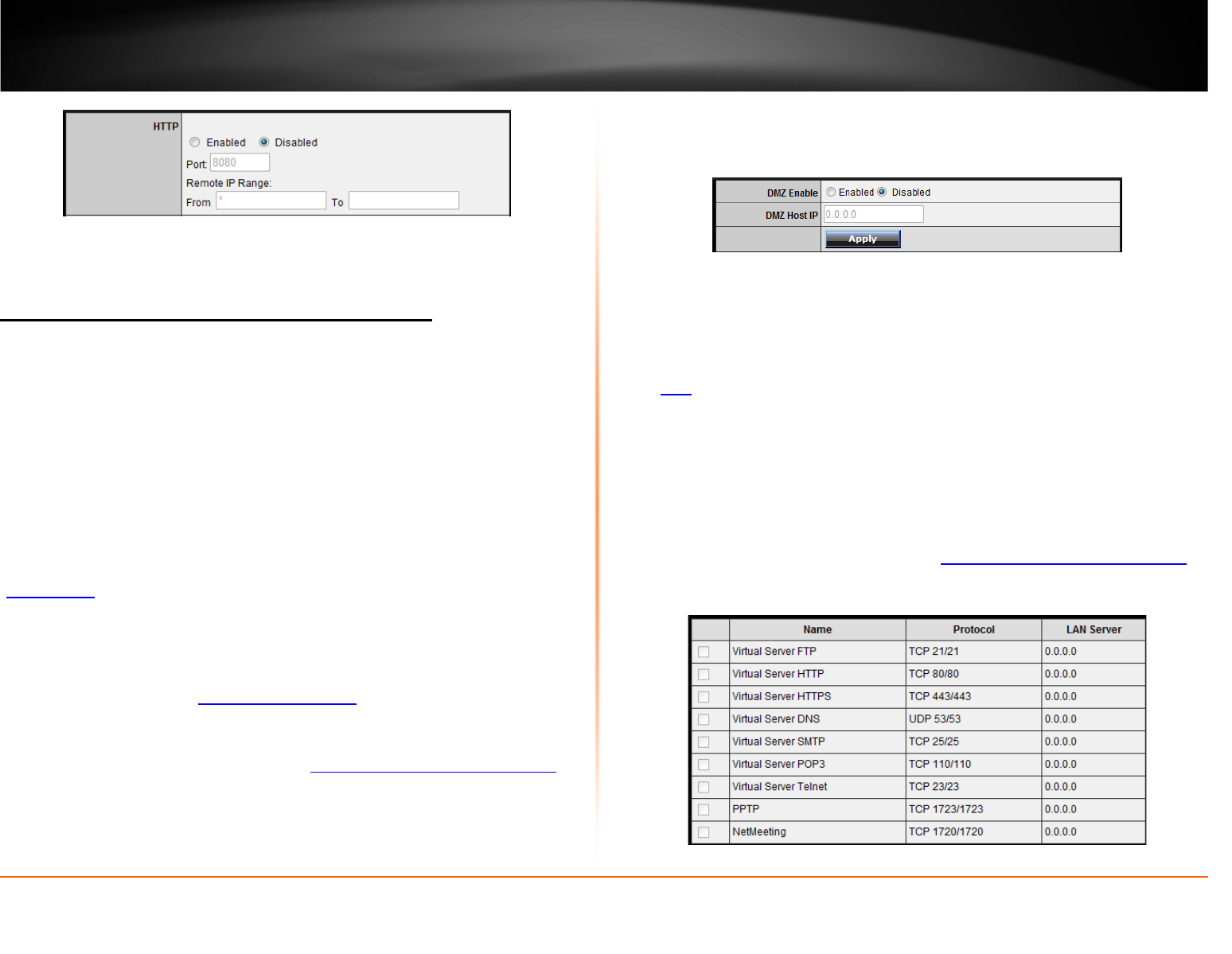
DMZ
Access > DMZ
You may want to expose a specific computer or device on your network to the Internet
to allow anyone to access it. Your router includes the DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) feature
that makes all the ports and services available on the WAN/Internet side of the router
and forwards them to a single IP address (computer or network device) on your
network. The DMZ feature is an easy way of allowing access from the Internet however,
it is a very insecure technology and will open local area network to greater threats from
Internet attacks.
It is strongly recommended to use Virtual Server (also called port forwarding, see
“
Virtual Server” on page 31) to allow access to your computers or network devices from
the Internet.
1. Make the computer or network device (for which you are establishing a DMZ link) has
a static IP address (or you can use the DHCP reservation feature to ensure the device
has a fixed IP address) (see “
Set up DHCP reservation” on page 28).
A. Signing up for a Dynamic DNS service (outlined in the DDNS section) will
provide identification of the router’s network from the Internet.
2. Log into your router management page (see “
Access your router management page”
on page 24).
3. Click on Access, and click on DMZ.
4. Next to DMZ Enable, click Enabled.
5. Next to DMZ Host IP, enter the IP address you assigned to the computer or network
device to expose to the Internet.
6. To save changes, click Apply.
Virtual Server
Access > Virtual Server
Virtual Server (also called port forwarding) allows you to define specific ports (used or
required by a specific application) and forward them to a single IP address (a computer
or device) on your network. Using this feature is more secure compared to using DMZ
(see
DMZ on page 31) in which DMZ forwards all ports instead of only specific ports
used by an application. An example would be forwarding a port to an IP camera
(TRENDnet IP cameras default to HTTP TCP port 80 for remote access web requests) on
your network to be able to view it over the Internet.
Since most ISPs constantly change your home IP address, to be able to access the Virtual
Server port(s) from the Internet it is recommended to setup Dynamic DNS service (See
DynDNS section).
1. Log into your router management page (see “
Access your router management page”
on page 24).
2. Click on Access, and click on Virtual Server.
