5
To prevent back-drafts, a
damper at the duct outlet
may also be required.
When planning new duct
work, always look for
the shortest, most direct
route to the outside.
Venting can be done
through the roof or
directly through the back
wall to the outside.
Make sure duct work
does not interfere with floor joists or wall studs.
Calculating the Maximum Duct Run Length
The maximum straight duct length for the hood is 100
feet. For each elbow and transition added to the duct
work, a certain number of feet must be subtracted from
the maximum straight length to compensate for wind
resistance. To determine the length the duct work cannot
exceed, subtract all of the equivalent lengths of the elbows
and transitions listed below from 100 feet.
Duct Work Equivalent Lengths
DUCT PIECE SUBTRACT
90° elbow 15 feet
45° elbow 9 feet
3 1/4” x 10” to 8” round 1 foot
Wall cap with damper 30 feet
Roof cap 30 feet
Duct Work Design Tips
Wherever possible, reduce the number of transitions
and turns to as few sharp angles as possible. Two
staggered 45° angles are better than one 90°. Keep
turns as far away from the hood exhaust as possible,
with as much space between each bend as possible.
For best performance, use round duct instead of
rectangular, especially when elbows are required.
If multiple elbows are used, try to keep a minimum of
24” of straight duct between them. Avoid “S” or “back to
back” configurations of adjacent elbows.
In regions where the weather gets extremely cold,
thermal breaks, such as a short section of non-metallic
duct, should be used to avoid indoor heat loss. The
break should be located as close to the pass through
point to the outside as possible.
Do not use flexible metal duct.
Do not use duct work that is smaller in cross-sectional
area than the recommended size duct (8” round).
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Electrical Power Supply
WARNING
Observe all governing codes and ordinances during
planning and installation. Contact your local building
department for further information.
•
Electrical Specifications
It is the owner’s responsibility to ensure that the electrical
connection of this appliance is performed by a qualified
electrician. The electrical installation, including minimum
supply wire size and grounding, must be in accordance with
the National Electric code ANSI/NFPA* (or latest revision)
and local codes and ordinances.
*A copy of the standard may be obtained from:
National Fire Protection Association
1 Batterymarch Park
Quincy, Massachusetts 02269-9101
This hood requires a dedicated 120 Vac, 60Hz, 15 A circuit.
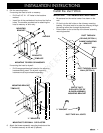
Plan the Duct Work Installation
WARNING
To reduce the risk of fire and to properly exhaust
air, be sure to duct air outside the house or building.
Do not vent exhaust air into spaces within walls or
ceilings or into attics, crawl spaces or garages.
Tape all duct joints securely to prevent combustion
by-products, smoke or odors from entering the home.
Doing so will also improve system efficiency.
Do not exhaust more than one vent into a single duct
run.
Use only duct work constructed of materials deemed
acceptable by state, municipal and local codes.
Range hoods may interrupt the proper flow of
smoke and combustion gases from furnaces, gas
water heaters and fireplaces. To avoid drawing
lethal gases into the home, follow the manufactures
recommendation for these devices and consult NFPA
and ASHRAE recommendations.
•
•
•
•
•
All duct work materials (including screws and duct tape)
must be purchased separately by the customer.
The hood exhaust connects to an 8-inch round duct.
You can increase the duct size over the duct run if
desired. To prevent a back draft, never decrease the
duct size over the run.
Do not rely on duct tape alone to seal duct joints.
Fasten all connections with sheet metal screws and
tape all joints with certified silver tape or duct tape.
Use sheet metal screws as require to support the duct
weight.
•
•
•
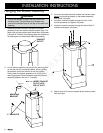
PREPARING FOR INSTALLATION