ZENworks® ESM 3.5 Administrator’s Manual 10
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management
Novell's ZENworks Endpoint Security Management (ESM) provides complete, centralized
security management for all endpoints in the enterprise. Because ESM applies security at the most
vulnerable point, the endpoint, all security settings are applied and enforced regardless of whether
the user is connecting to the network directly, dialing in remotely, or even not connecting to
corporate infrastructure at all. This is critical to not only protect the data within the corporate
perimeter, but also to protect the critical data that resides on the endpoint device itself.
ESM automatically adjusts security settings and user permissions based on the current network
environment characteristics. A sophisticated engine is used to determine the user's location and
automatically adjusts firewall settings and permissions for applications, adapters, hardware, etc.
Security is enforced through the creation and distribution of ESM security policies. Each location
(Work, Home, Alternate, Airport, etc.) listed in a security policy is assigned to a network
environment (or multiple network environments). A location determines which hardware is
available and the degree of firewall settings that are activated within the network environment.
The firewall settings determine which networking ports, access control lists (ACLs), and
applications are accessible/required. Various integrity checks and scripts can be run at location
change to ensure that all required security software is up to date and running.
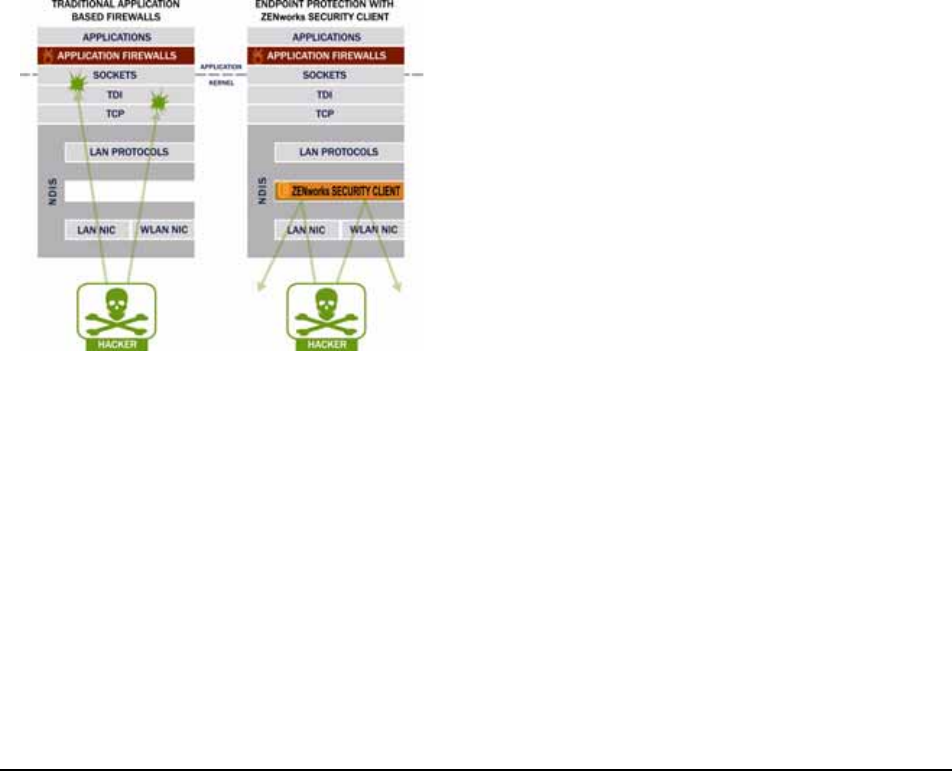
In securing mobile devices, ESM is superior to
typical personal firewall technologies which operate
only in the application layer or as a firewall-hook
driver. ESM client security is integrated into the
Network Driver Interface Specification (NDIS)
driver for each network interface card (NIC),
providing security protection from the moment
traffic enters the PC. Differences between ESM and
application-layer firewalls and filter drivers are
illustrated in Figure 1.
Security decisions and system performance are
optimized when security implementations operate at
the lowest appropriate layer of the protocol stack.
With ESM's ZENworks Security Client, unsolicited
traffic is dropped at the lowest levels of the NDIS driver stack by means of Adaptive Port
Blocking (stateful packet inspection) technology. This approach protects against protocol-based
attacks including unauthorized port scans, SYN Flood, NetBIOS, and DDOS attacks.
Figure 1 : Effectiveness of NDIS-layer firewall
