INTRODUCTION Eskimo Ice Installation & Operation Manual
2 L-3152 ENGLISH
ICE MAKING AND REFRIGERATION BASICS
HOW THE EI1000D MAKES ICE
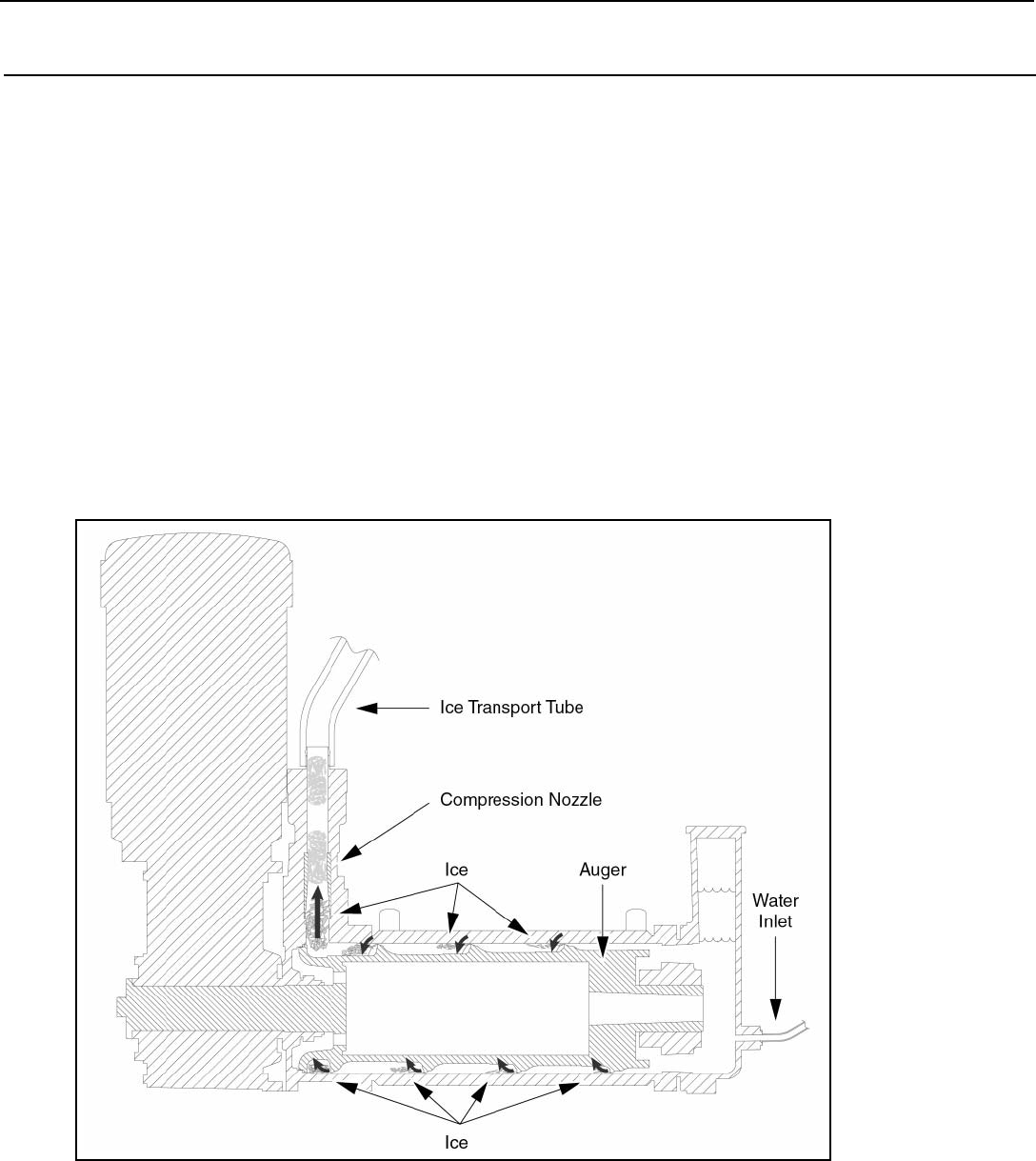
Ice production is continuous.
Fresh water floods the cylindrical evaporator. Using a refrigeration process, heat is removed from the fresh water in order to
freeze it on the inner surface.
A rotating auger continuously scrapes ice from the inner wall of the evaporator and moves the harvested ice through the
evaporator into an ice extrusion canal. There the ice is forced through a restrictive nozzle that squeezes out the water and
creates the ice. The continuous extrusion process pushes the ices through a transport tube which runs to the ice-collection box.
See Figure 1.
A solid-state PC board controls and monitors the functionality of the ice machine. In addition to sequencing electrical
components, the board monitors various operational parameters. A full complement of indicator lights and digital display allow
visual status of the machine’s operation.
A unique spout-clog detection system is incorporated in the Eskimo Ice machine. A switch located at the ice-discharge port of
the machine detects the position of the transport tube. If the hose clogs with ice, the transport tube moves out of the normal
running position, and the switch turns the ice maker off.
Figure 1: Ice-Making Process
THE REFRIGERATION PROCESS
The basic principle of an ice machine system is that a liquid refrigerant absorbs heat as it turns into a gaseous state
(evaporates) and releases heat as it turns back into a liquid state (condenses). The system consists of five main components:
• Evaporator - Absorbs heat from the fresh water in the evaporator shell causing the fresh water to freeze.
• Auger - Scrapes the frozen fresh water from the interior sides of the evaporator shell and extrudes it into the discharge
hose.
• Condenser - Releases heat into the system’s circulating seawater and turns the refrigerant gas back into a liquid.
• Compressor - Drives the refrigerant through the loop.
• Metering Device - Meters the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator.