24
FAILSAFE OF THE SYSTEM WHICH USES THE INVERTER
4 FAILSAFE OF THE SYSTEM WHICH USES THE INVERTER
When a fault occurs, the inverter trips to output a fault signal. However, a fault output signal may not be output at an inverter
fault occurrence when the detection circuit or output circuit fails, etc. Although Mitsubishi assures best quality products,
provide an interlock which uses inverter status output signals to prevent accidents such as damage to machine when the
inverter fails for some reason and at the same time consider the system configuration where failsafe from outside the inverter,
without using the inverter, is enabled even if the inverter fails.
(1) Interlock method which uses the inverter status output signals
By providing interlocks, inverter fault can be detected. For the interlocks, use different status output signals of the
inverter (virtual terminals of the CC-Link communication) in combinations shown below.
(2) Backup method outside the inverter
Even if the interlock is provided by the inverter status signal, enough failsafe is not ensured depending on the failure
status of the inverter itself. For example, even if the interlock is provided using the inverter fault output signal, start signal
and RUN signal output, there is a case where a fault output signal is not output and RUN signal is kept output even if an
inverter fault occurs.
Provide a speed detector to detect the motor speed and current detector to detect the motor current and consider the
backup system such as checking up as below according to the level of importance of the system.
1)Start signal and actual operation check
Check the motor running and motor current while the start signal is input to the inverter by comparing the start signal to
the inverter and detected speed of the speed detector or detected current of the current detector. Note that the motor
current runs as the motor is running for the period until the motor stops since the inverter starts decelerating even if the
start signal turns off. For the logic check, configure a sequence considering the inverter deceleration time. In addition, it is
recommended to check the three-phase current when using the current detector.
2) Command speed and actual operation check
Check if there is no gap between the actual speed and commanded speed by comparing the inverter speed command
and detected speed of the speed detector.
No. Interlock Method Check Method Used Signals Refer to Page
1)
Inverter protective
function operation
Operation check of an alarm contact
Circuit error detection by negative logic
Fault output signal
(ALM signal)
Refer to Chapter 4
of the Instruction
Manual (Applied).
2) Inverter running status Check of the reset release signal
Reset release signal
(RY signal)
Refer to Chapter 4
of the Instruction
Manual (Applied).
3) Inverter running status
Logic check of the start signal and
running signal
Start signal
(STF signal, STR signal)
Running signal (RUN signal)
Refer to Chapter 4
of the Instruction
Manual (Applied).
4) Inverter running status
Logic check of the start signal and
output current
Start signal
(STF signal, STR signal)
Output current detection signal
(Y12 signal)
Refer to Chapter 4
of the Instruction
Manual (Applied).
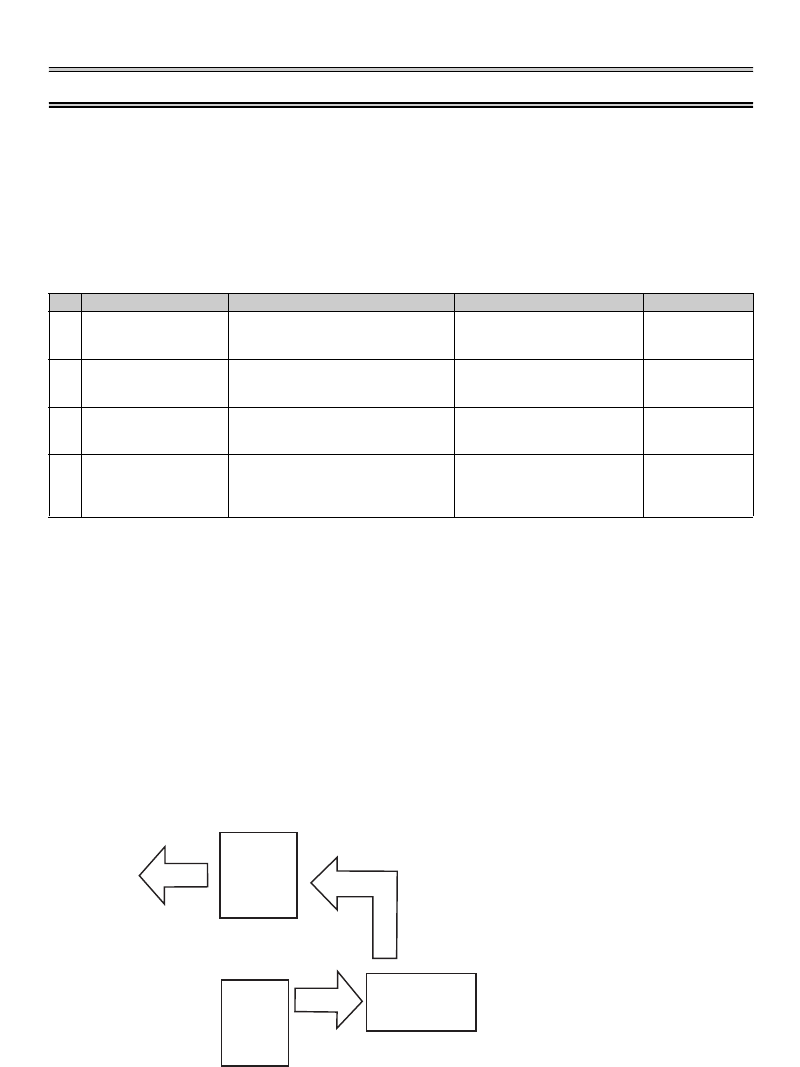
Inverter
Controller
System failure
To the alarm detection sensor
Sensor
(speed, temperature,
air volume, etc.)