English Cookbook
English Cookbook
- En-11 -
Introduction
Cooking with Microwave Energy
Microwaves are a form of high frequency electromagnetic waves (approx 12cm wavelength) similar to those used by a
radio. Electricity is converted into microwave energy by the magnetron tube. The microwaves travel from the
magnetron tube to the oven cavity where they are reflected, transmitted or absorbed.
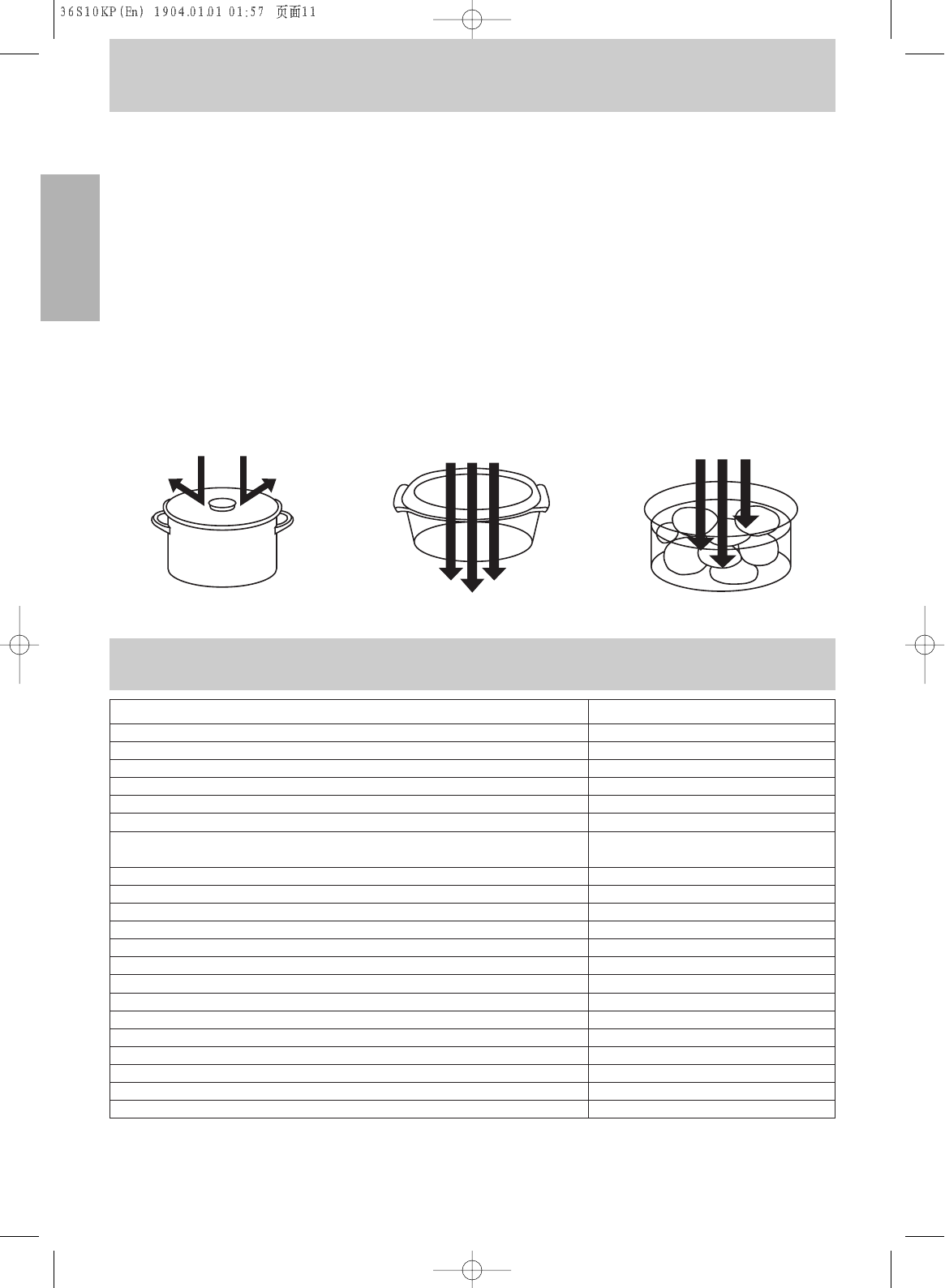
Reflection
Microwaves are reflected by metal
just as a ball is bounced off a wall.
A combination of stationary (interior
walls) and rotating metal (turntable
or stirrer fan) helps assure that the
microwaves are well distributed
within the oven cavity to produce
even cooking.
Transmission
Microwaves pass through some
materials such as paper, glass and
plastic much like sunlight shining
through a window. Because these
substances do not absorb or reflect
the microwave energy, they are ideal
materials for microwave oven
cooking containers.
Absorption
Microwaves are absorbed by food.
They penetrate to a depth of about 2
to 4cm. Microwave energy excites
the molecules in the food (especially
water, fat and sugar molecules), and
causes them to vibrate very quickly.
The vibration causes friction and
heat is produced. In large foods, the
heat which is produced by friction is
conducted to the center to finish
cooking.
Cookware and Utensil Guide
Microwave Oven
Aluminuim Foil For Shielding
Grill Tray No
Browning Dish Yes
Browning Paper Bags No
Dinnerware: Oven/Microwave Safe Yes
Non Oven/Microwave Safe No
Disposable Polyeser Yes
Paperboard Dishes
Glassware: Oven Glassware & Ceramic Yes
Non-heat Resistant No
Metal Cookware No
Metal Twist-ties No
Oven Cooking Bag Yes
Oven Rack No
Paper Towels and Napkins Yes
Plastic Dishes: Microwave Safe Yes
Non-microwave Safe No
Plastic Wrap Yes
Straw, Wicker, Wood Yes
Thermometers: Microwave Safe Yes
Conventional No
Wax Paper Yes