C141-E124-01EN1 - 4
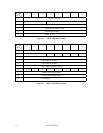
b. Command code
Command code specifies the type of command in each group.
(2) LUN (Logical Unit Number)
This field specifies the address of the logical unit (device) connected under the TARG in cases
where the IDENTIFY message is not used. If the IDENTIFY message is used, the value of the
CDB’s LUN field is ignored when the LUN is specified.
Note:
It is possible that the definition of this field may be changed in future SCSI standards. It is
recommended that the LUN be specified using the IDENTIFY message, and that a zero be
specified in this CDB field.
(3) Logical block address
This field shows the leading logical data block address of the data block on the disk media to be
processed by the command. In the group 0 CDB, 21-bit block addressing is possible and in the
group 1, group 2 and group 5 CDBs, 32-bit block addressing is possible. Specifications for logical
data block addressing in the IDD are described in Section 1.8.
(4) Transfer data length
In this field, the length of data to be transferred between INIT and TARG when the command is
executed is specified by the number of logical data blocks or the number of bytes. In subsequent
descriptions, the former is called the “transfer block count” and the latter is called the “transfer
byte length” or “parameter list length.”
Furthermore, this field may be used with a different meaning, or it may not have any meaning at
all, depending on the type of command. There are also some commands which allocate 3 or more
bytes as the transfer data length field. Detailed specifications of these commands are described in
the individual command specifications in Chapter 3.
a. Transfer block count
When the “Transfer Data Length” is specified as the “Transfer Block Count,” this field
specifies the number of logical data blocks to be transferred between INIT and the IDD.
In commands where this field is 1 byte in length, if the field’s specified value is 0, it is
regarded as specifying 256 blocks, and it is possible to specify a block count ranging from 1 to
256 blocks. On the other hand, in commands where this field is 2 bytes in length, if the field’s
specified value is 0, no data transfer is executed. It is possible to specify a block count ranging
from 0 to 65,535 blocks.