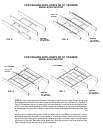
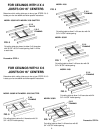
(1/2 A X B = AREA Sq. Ft.)
GABLE EXHAUST
(A X B = AREA Sq. Ft.)
EAVE
EXHAUST
(A X B = AREA Sq. Ft.)
GABLE EXHAUST
ATTIC AIR INTAKE AND DISCHARGE
Your Whole House Ventilator will be discharging a large volume of air into the attic every minute.
Provisions must be made to allow this air to escape to the outside. The sketches below illustrate
several different types of exhaust vents that are in common usage. Of these types, the under-eave
and gable methods are the most prevalent. Under-eave is probably the most satisfactory from the
standpoint of simplicity and economical installation. Make sure under-eave vents are not blocked
with ceiling insulation. The fan requires a given amount of exhaust outlet in order to ensure quiet
operation and unrestricted air movement. The table below shows the minimum area required for
proper operation of fan. Sufficient ventilation is very important. Unless enough is provided, the fan
motor will run hot, activating the thermal protector and shutting off the motor. When it cools, it will
restart. Such intermittent operation is usually an indication of too little outlet air or too little intake
air through the house.
MINIMUM ATTIC DISCHARGE AREAS REQUIRED
(All areas are in square feet)
FAN UNRESTRICTED* WOOD LOUVRE* METAL LOUVRE* SHUTTERS
SIZE OPENING REQD. OPENING REQD. OPENING REQD. AUTO. MAN. ETC.
24” 6.5 14.7 11.4 4
30” 9.2 20.7 16 6.3
36” 12 27 21 9
*If fly screen is used, double these values. If 1/2” hardware cloth or large mesh expanded metal are
used, the values given are sufficiently large. If no screen used, reduce values shown by 20%.
B (Ft.)
B (Ft.)
B (Ft.)
A (Ft.)
A (Ft.)
A (Ft.)
2