6
between the hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and the hypochlorite ions
(OCl
-
).
Although both forms are considered free chlorine, it is the hypochlorous
acid that provides the strongest disinfecting and oxidising characteristic
of chlorine solutions.
The amount of hypochlorous acid in chlorinated water dependends upon
the pH value of the solution. Changes in pH value will effect the HOCl
equilibrium in relation to the hydrogen and hypochlorite ion.
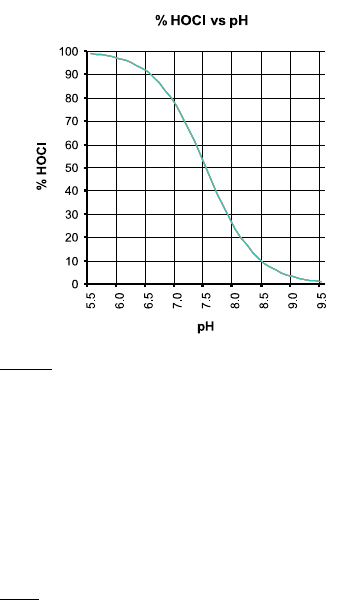
As depicted by the curve below, HOCl decreases and OCl
-
increases as pH
increases. At a low pH, almost all the free chlorine is in the molecular
form HOCl and at a pH of around 7.5, the ratio between HOCl and OCl
-
is
50:50. Since the ionic form OCl
-
is a slow acting sanitizer while the
molecular HOCl is a fast acting, it is important to measure regularly the
pH. As a general rule a pH of about 7.2 is recommended to maintain fast
acting disinfection conditions.
Bromine
In many countries bromine sanitizing has been introduced as an
alternative for chlorine, although it is a less strong sanitizer. The advantage
of bromine is its stability at higher temperatures (advantageous for hot
well pools), and its maintained disinfection power at higher pH. Further
it does hardly react with nitrogen compounds, reducing the unpleasant
odour, and eye irritation problems. The main disadvantage of bromine is
the slower acting disinfecting power, making it less suitable for larger
pools.
Ozone
Ozone is a very strong oxidizing agent that does destroy most difficult to
oxidize organic compounds and chloramines. It thus allows the pool
manager to remove very efficiently combined chlorine without refreshing
