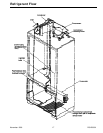
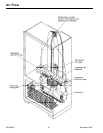
November 1996 11 RS1200001
System Diagnosis
Refrigerant Overcharge Symptoms
• Above normal freezer temperature.
• Compressor running continuously.
• Freezing in refrigerator due to Chef’s Pantry
™
.• High suction and head pressure.
• High wattage.
• Warm evaporator inlet and outlet temperature.
• Below ambient suction tube temperature. Check for
separated heat exchanger when suction temperature
is colder than ambient.
• Refrigerant will flood out causing suction line to frost
or sweat, if defrost system fails and cooling coil is not
defrosted. Correct problem instead of purging
refrigerant.
• Freezer colder than necessary (normal package
temperature is 0° to 2°F).
• Evaporator fan motor not running.
Refrigerant Shortage Symptoms
• Rise in refrigerator and freezer temperatures.
Warm beverages will be first indication of
possible refrigerant shortage. Frozen meats and
vegetables will not thaw immediately. Some freezing
may occur in refrigerator section due to additional run
time because of Chef’s Pantry
™
. Capillary line will not
have full column of liquid with refrigerant shortage. A
noticeable hissing sound in evaporator will be heard.
Hissing should not be mistaken for regular refrigerant
boiling sounds.
• Long or continuous run time.
• Traces of oil caused by leak or cracked refrigerant
line.
• Lower than normal wattage.
• Compressor will feel hot due to heat generated by
motor windings from continuous running. Compressor
will not be as hot as it would be with full charge and
long run times caused by reasons such as dirty
condenser.
• Condenser will feel room temperature.
• Capillary tube will feel warmer than normal.
• If high side leak, both gauges will show lower than
normal readings. As charge becomes less, readings
will lower. Suction pressure gauge will probably
indicate a vacuum.
• If low side leak, suction pressure gauge will show
lower than normal readings, probably in a vacuum.
Head pressure gauge will show higher than normal.
Readings will probably rise because of air drawn in
through leak is compressed by compressor and
accumulates in high side (condenser) of system.
• Partial frosting of evaporator.
Restriction Symptoms
• Refrigeration cooling occurs on low pressure side of
partial restriction.
• Total restriction will stop circulation of refrigerant and
no cooling will occur.
• Touch refrigeration lines. Most common place for
restriction is at drier filter or capillary tube inlet or
outlet.
• If partial restriction there will be temperature
difference at restriction point. Evaporator side will be
cooler. In most cases, frost and/or condensation will
be present. Longer time is required for system to
equalize.
• Kinked line will cause restriction. Visually check entire
system for kinks.
• Slight restriction will give same indications as
refrigerant shortage with lower than normal back
pressure, head pressure, wattage, and warmer
temperatures.
• If total restriction is on discharge side of compressor,
higher than normal head pressures and wattages will
occur. This is only true while low side is being pumped
out and if restriction was between compressor and
first half of condenser.
Diagnose restriction by completing the following:
1. Discharge system.
2. Replace drier-filter.
3. Evacuate and recharge system with specified
refrigerant charge.
If refrigerator performs normally, the following
conditions may exist:
• refrigerant loss
• partially restricted drier
• moisture in system
If refrigerator performs as previously described,
capillary line or condenser may be restricted. Locate
and correct restriction point.
Restriction reduces refrigerant flow rate and heat
removal rate. Total restriction may be caused by
moisture, poorly soldered joint, or solid contaminants
in system. Moisture freezes at evaporator inlet end of
capillary tube. Solid contaminants collect in drier.
Wattage drops because compressor is not circulating
normal amount of refrigerant.
If restriction is on low side suction, pressure will be in
a vacuum and head pressure will be near normal. If
restriction is on high side, suction pressure will be in a
vacuum and head pressure will be higher than normal
during pump out period. In both cases, it will take
longer than 10 minutes for head pressure to equalize
with low side after compressor stops.