Component Function and Testing
April 1998 21 RS1200001 Rev.1
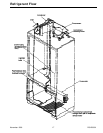
Condenser
Drier
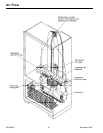
Evaporator
Heater,
evaporator
(defrost)
Ice Maker
See "Electronic Functional Description, Adaptive
Defrost Circuitry"
Check resistance across heater.
Check defrost system by thermocoupling defrost thermostat and plugging
refrigerator in wattmeter. Force into defrost mode. Wattmeter should read
specified watts (according to tech sheet) ± 20 watts. When defrost
thermostat reaches specified temperature (according to tech sheet) ±
5°F., thermostat should interrupt power to heater.
Leaks in evaporator can usually be detected by the use of electronic leak
detector or soap solution. Compressor oil is circulated with refrigerant so
look for oil when checking for leaks.
For minute leaks separate condenser from rest of refrigeration system
and pressurize condenser up to a maximum of 140 PSI with a refrigerant
and dry nitrogen combination. Recheck for leaks.
Inner volume of evaporator allows liquified refrigerant
discharged from capillary to expand into refrigerant
gas.
Act of expansion cools evaporate tube and fin
temperature to approximately -20°F, transfering heat
from freezer section to refrigerant.
Passing through suction line to compressor, the
refrigerant picks up superheat (a relationship between
pressure and temperature that assures complete
vaporization of liquid refrigerant) as result of capillary
being soldered to suction line.
Refrigerant gas is pulled through suction line by
compressor to complete refrigerant cycle.
Drier is placed at P.C. loop outlet and passes liquified refrigerant to
capillary.
Drier must be changed whenever sealed refrigeration system is opened.
Drier used in R12 sealed system is not interchangeable with drier used in
R134a sealed system. Replace drier with part #B2150504.
Condenser is a tube and wire construction located in
compressor compartment. Condenser is on high
pressure discharge side of compressor.
Refrigerant flows from compressor into a pre-
condenser serpentine below drain pan to evaporate
defrost water. From serpentine, refrigerant flows into
pre-condenser loop (Yoder loop) foamed around
freezer door opening to help control external
condensation around freezer door and on flange.
Higher pressure refrigerant gas is routed to condenser
where as gas temperature is reduced, gas condenses
into high pressure liquid state. Heat transfer takes place
because discharged gas is at higher temperature than
air that is passing over condenser.
Condenser is air cooled by fan motor. It is very
important that adequate air flow over condenser is
maintained. If efficiency of heat transfer from
condenser to surrounding air is impaired, condensing
temperature becomes higher. Higher temperature liquid
means less heat will be removed during boiling in
evaporation. This is indicated by higher that normal
head pressures, long run time, and high wattage.
Remove any lint, dust accumulation, etc. that would
restrict normal air movement throughout the condenser.
• Leaks in condenser can usually be detected by using an electronic
leak detector or soap solution. Look for signs of compressor oil when
checking for leaks. A certain amount of compressor oil is circulated
with refrigerant.
• Leaks in post condenser loop are rare as loop is a 1 piece copper
tube.
• In cases of minute leaks it may be necessary to separate condenser
from rest of refrigeration system and pressurize condenser up to a
maximum of 235 PSI with a refrigerant and dry nitrogen combination.
WARNING
To avoid severe personal injury or death observe the following:
• Protect against a sudden eruption if high pressures are
required for leak checking.
• High pressure compressed cases should never be used in
refrigeration systems without a reliable pressure regulator and
pressure relief valve in the lines.
Desiccant
(20) 8 X 12 4AXH - 7 M.S. - Grams
See “Ice Maker” section for service information.