Component Function and Testing
RS1200001 Rev. 1 20 April 1998
Capacitor Run capacitor connects to relay terminal.
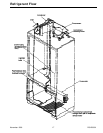
Capillary tube
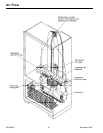
Compressor When compressor electrical circuit is energized, the
start winding current causes PTC relay to heat. After an
amount of starting time the start winding circuit turns
off. PTC relay will switch off the start winding circuit
even though compressor has not started (as when
attempting to restart after momentary power
interruption).
With "open" PTC relay, compressor will not start
because there is little or no current to start windings.
Overload protector will open due to high locked rotor
run winding current.
With "shorted" PTC relay or capacitor, compressor will
start and overload protector will quickly open due to
high current of combined run and start windings.
With open or weak capacitor, the compressor will start
and run as normal but will consume more energy.
Check for resistance between:
Terminals "S" & "C"
Terminals "R"& "C"
Ground Test
Disconnect power to refrigerator .Remove compressor leads and use an
ohmmeter set on highest scale. Touch 1 lead to compressor body (clean
point of contact) and the other probe to each compressor terminal. If a
reading is obtained, compressor is grounded and must be replaced.
1. Disconnect power to refrigerator.
2. Remove capacitor and disconnect capacitor wires.
3. Discharge capacitor by shorting across terminals with a resistor for
1 minute.
4. Check resistance across capacitor terminals with ohmeter set on
"X1K" scale.
• Needle should jump towards 0 ohms and quickly move back to
infinity.
• If needle does not move, the capacitor is open.
• If needle reads a constant value at or near 0 ohms, the capacitor is
shorted.
• If needle jumps towards 0 and then moves back to a constant high
resistance (not infinity), the capacitor has a high resistance leak.
Operation Test
If motor winding tests fail to show cause for failure:
1. Disconnect power to refrigerator. Wire a test cord to disconnect
switch.
2. Place time delayed fuse, with U.L. rating equal to amp rating of motor,
in test cord socket.
3. Remove overload and relay.
4. Connect start, common, and run leads of test cord on appropriate
terminals of compressor.
5. Attach capacitor leads of test cord together. If capacitor is used,
attach capacitor leads to a good capacitor of same capacity.
6. Plug test cord into volt-watt meter to determine start and run wattage
as well as check for low voltage which can also be a source of
trouble.
7. With power to volt-meter, press start cord switch and release. If
compressor motor starts and draws normal wattage compressor is
okay and trouble is in capacitor, relay, overload, freezer temperature
control, adaptive defrost control, or elsewhere.
Capillary is sized in diameter and length to
feed proper amount of refrigerant to
evaporator.
Capillary is soldered to suction line to transfer
heat from capillary and add additional
superheat to gas refrigerant in compressor
suction line.
Capillary discharges into evaporator.
WARNING
To avoid electrical shock which can cause severe personal
injury or death, discharge capacitor through a resistor before
handling.