1-31
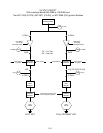
A bell crank style basket lift consists of a cam and bell
crank that are connected to the basket lift arm by a flat metal
link. The cam is attached to a drive motor. The motor ro-
tates the cam, thus raising or lowering the lift arm linked to
the bell crank. A roller-activated microswitch is used to limit
travel. When the roller in the microswitch is in contact with
the cam, the motor is energized. As the cam rotates, the mi-
croswitch roller eventually loses contact with the cam and
the circuit is broken, de-energizing the motor.
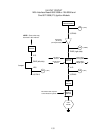
Timing circuitry in the controller initiates and stops basket
lift operation depending upon the variables programmed by
the operator. When the product button is pressed, the timing
circuitry activates a coil in the basket lift relay to supply
power to the motor. The microswitch stops the motor at the
lift’s lower travel limit and the switch contacts are reversed. At the end of the programmed cooking
time, the timing circuit activates the coil once more and the lift rises until the microswitch again
loses contact with the cam, opening the circuit and stopping the motor.
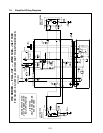
Problems with either basket lift design can be grouped into three categories:
• Binding/jamming problems
• Motor and gear problems
• Electronics problems
BINDING/JAMMING PROBLEMS
Noisy, jerky or erratic movement of the lifts is usually due to lack of lubrication of the rods and their
bushings. Apply a light coat of Lubriplate
®
or similar lightweight white grease to the rod and
bushings to correct the problem.
With the modular basket lift, another possible cause of binding is improper positioning of the motor,
which prevents the gear from correctly engaging the teeth in the rod. To correct the problem, loosen
the screws that hold the motor in place and move it forward or backward until the rod has just
enough slack to be rotated slightly.
MOTOR AND GEAR PROBLEMS
With the modular basket lift, the most likely problem to be encountered in this category is erratic
motion of the lift due to a worn drive gear. Failure to keep the lift rod and bushings properly
lubricated will cause unnecessary wear of the gear. The problem is corrected by replacing the worn
gear.
If the lift cycles correctly but fails to remain in the up position (i.e., goes up, but then slowly settles
back down into the frypot), the problem is a failed motor brake. A failed motor brake cannot be
repaired and requires replacement of the motor itself.
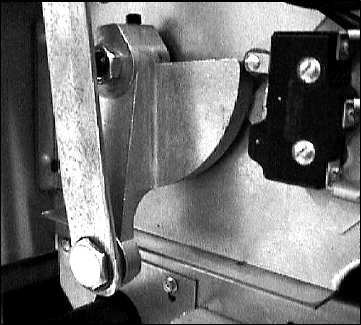
Bell crank and cam with basket lift
link shown in down position. Note
microswitch in upper right corner.