16
Cooking Utensils
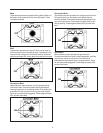
• Use proper pan size. Do not use utensils that overhang
element by more than 1 inch.
More than 1" overhang
2"
Less than 1" overhang
1"
• Use care when using glazed cooking utensils. Some
glass, earthenware, or other glazed utensils break due
to sudden temperature changes.
• Select utensils without broken or loose handles.
Handles should not be heavy enough to tilt pan.
• Select utensils with flat bottoms.
• Do not use a wok with a ring stand.
Do not use a wok with
a ring stand.
Use a flat
bottom wok.
For best cooking results, use a pan with a flat bottom.
Determine if pan has a flat bottom.
1. Rotate a ruler along bottom of pan. If pan is not flat,
gaps between bottom of pan and edge of ruler occur.
2. A small groove or mark on a pan does not effect
cooking times. However, if a pan has a gap, formed
rings, or an uneven bottom, it does not cook
efficiently and in some cases may not boil liquid.
Utensils
Utensil Material Charateristics
Type Temperature
Response
Uses
Aluminum Heats and Cools
Quickly
Frying,
Braising,
Roasting
Cast Iron Heats and Cools
Slowly
Low Heat
Cooking,
Frying
Copper
Tin Lined
Heats and Cools
Quickly
Gourmet
Cooking, Wine
Sauces, Egg
Dishes
Enamelware Depends on Base
Metal
Low Heat
Cooking
Ceramic (Glass) Heats and Cools
Slowly
Low Heat
Cooking
Stainless Steel Heats and Cools at
Moderate Rate
Soups,
Sauces,
Vegetables,
General
Cooking