CY4672 Reference Design Guide, Document # 001-16968 Revision ** 17
WirelessUSB™ Protocol 2.2
2.2.2 Idle Mode (HID only)
The HID enters this mode after a power on reset before it has had any communication with the RDK
bridge. If the bridge’s MID is stored in non-volatile memory the HID retrieves the bridge’s MID, calcu-
late the network ID and move to reconnect mode. If the bridge’s MID is not stored in non-volatile
memory the HID waits in idle mode until a user-initiated event causes the HID to enter bind mode.
After a defined period of time in idle mode the HID goes to sleep in order to conserve power. When
the HID wakes up due to a user action, it re-enters Idle mode.
2.2.3 Reconnect Mode (HID only)
Reconnect mode is used by the HID to discover the current channel used by the bridge and to estab-
lish a connection with the bridge. Upon entering reconnect mode the HID uses the network ID to
select a channel using the channel selection algorithm. The HID transmits ‘connect requests’ con-
taining the manufacturing ID of the desired bridge and listens for an AutoACK. If an AutoACK is
received the HID disables the AutoACK and continues to listen for a ‘connect response’. If a bridge
in data mode receives a ‘connect request’ containing its manufacturing ID, it sends a positive ‘con-
nect response’ to the HID. If a HID receives a positive ‘connect response’ it moves to data mode. If a
HID does not receive a positive ‘connect response’, it selects the next channel using the channel
selection algorithm and repeats the procedure. If the HID does not receive a positive ‘connect
response’ on any of the channels in the subset, it enters goes to sleep in order to conserve power.
When the HID wakes up due to a user action it reenters reconnect mode.
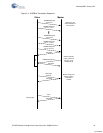
2.2.4 Button Bind Mode
HID
Bind mode allows the HID to retrieve the bridge’s manufacturing ID which is used to calculate the
network ID. Upon entering bind mode the HID sets the current channel and PN code to the channel
and PN code specified in the bind ID. The HID then transmits bind requests and listens for an
AutoACK. If an AutoACK is received, the HID (keeping the AutoACK enabled) continues to listen for
a bind response (containing the bridge’s MID) from the bridge. If a bind response is not received, the
HID moves to the next channel. If a bind response is received, the HID stores the bridge’s MID, cal-
culates the network ID, and moves to reconnect mode. The algorithms used to calculate these fields
are implementation specific and should be the same on the bridge and the HID (both devices use the
bridge’s manufacturing ID to calculate these fields). If a defined* period of time has elapsed while in
bind mode without receiving a bind response, the HID exits bind mode and restores the channel and
PN code settings that were in use prior to entering bind mode. Bind mode should last long enough
for the user to locate and push the button on both the bridge and the HID. A user-initiated event can
cause the HID to enter bind mode from any other mode.
[*The timeout value is configurable using the BIND_RETRY_COUNT define.]
Bridge
Upon entering bind mode the bridge sets the current channel and PN code to the channel and PN
code specified in the bind ID. The bridge listens for a bind request on each channel for approxi-
mately 320 ms before selecting the next channel using the channel selection algorithm. This reduces
the possibility of the bridge not receiving the bind request from the HID in the event of channel inter-
ference. If the bridge receives a bind request from the HID containing a supported device type, it
sends a bind response containing the bridge’s manufacturing ID and then switches to ping mode.
The bridge also switches to ping mode if the defined* time period has elapsed while in bind mode.
The channel selection algorithm uses the bind ID to produce the channel subset for bind mode.
[*The timeout value is configurable using the NUM_CHANNELS_PER_SUBSET define.]
[+] Feedback