Chapter 1 Getting Started
Operating the Counter
1-34 Operating Guide
1
NOTE For most of the Counter’s settings, when you continue to press either the
up-arrow or the down-arrow key when you reach the end of the available
settings, the value for the setting “rolls over” to the value at the opposite
end of the range. For example, if the GPIB address is set to 31, and you
press the up-arrow key, the value changes to one.
However, when you adjust the value in the units position for the number
of measurements to be averaged, rollover does not occur. If you press the
up-arrow when the value in the tens position is zero and the value in the
units position is nine, or if you press the down-arrow when the value in
the tens position is zero and the value in the units position is one, there is
no change. If the value in the units position could roll over (in either
direction), it would allow you to set a value of zero for the number of
averages. Since at least one measurement must be taken, zero is an
illegal value.
NOTE When the resolution setting is high (e.g., 1 Hz), and a large number of
averages is selected, it takes a considerable amount of time for the
Counter to take the measurements, compute the averages, and display a
reading. As a result, the rate at which the display is updated is
considerably slower than at small numbers of averages and lower
resolution settings. For example, when the resolution is set to 1 Hz,
and the number of averages is set to 60, a new reading is displayed every
60 seconds (approximately).
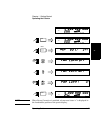
Setting the Resolution
Since less time is required to compute each measurement as the
resolution of the measurements is reduced, the resolution setting affects
the rate at which measurements are taken and displayed, as well as the
number of digits displayed for the measurements. As a result, the rate at
which the Gate indicator flashes changes when you change the resolution.
As shown in the procedure in the diagram on the next page, the available
resolution settings are 1 Hz (the default setting), 10 Hz, 100 Hz, 1 KHz,
10 KHz, 100 KHz, and 1 MHz.