Chapter 3 Programming Your Universal Counter for Remote Operation
Elements of SCPI Commands
Programming Guide 3-11
Parameter Types
Table 3-1 contains explanations and examples of parameter types. Parameter
types may be numeric value, Boolean , literal, NRf, string, non-decimal numeric,
or arbitrary block.
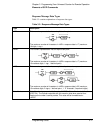
Table 3-1. Command and Query Parameter Types
TYPE EXPLANATIONS AND EXAMPLES
<numeric value>
<Boolean>
<literal>
<NRf>
<string>
<non-decimal
numeric>
<arbitrary block>
Accepts all commonly used decimal representation of numbers including optional signs, decimal
points, and scientific notation:
123, 123e2, -123, −1.23e2, .123, 1.23e −2, 1.23000E−01.
Special cases include MINimum and MAXimum as follows:
MINimum selects minimum value available.
MAXimum selects maximum value available.
Queries using MINimum or MAXimum return the associated numeric value.
Represents a single binary condition that is either true or false:
1 or ON, 0 or OFF (Query response returns only 1 or 0.)
An <NRf> is rounded to an integer. A non-zero value is interpreted as 1.
Selects from a finite number of choices. These parameters use mnemonics to represent each valid
setting. An example is the INPut:COUPling AC | DC command parameters (AC | DC).
Flexible numeric representation. Only positive integers are used for NRf parameters in the Counter.
A string parameter is delimited by either single quotes or double quotes. Within the quotes, any
characters in the ASCII 7-bit code may be specified.
The following HP BASIC program statement sends a command containing a <string> parameter:
OUTPUT 703;"FUNC ‘FREQ’"
Format for specifying hexadecimal (#H1F), octal (#Q1077), and binary (#B10101011) numbers
using ASCII characters. May be used in :STATus subsystem commands.
The syntax is a pound sign (#) followed by a non-zero digit representing the number of digits in the
subsequent decimal integer. The decimal integer specifies the number of
8-bit data bytes being sent. This is followed by the actual data. The terminator is a line feed
asserted with EOI. For example, for transmitting 8 bytes of data, the format could be:
The “2” indicates the number of digits that follow and the two digits “08” indicate the number of data
bytes to be transmitted.
A zero-length block has the format: #0<new line>^EOI
<new line> is defined as a single ASCII-encoded byte corresponding to 10 decimal.