Methods for Processing Disk Files
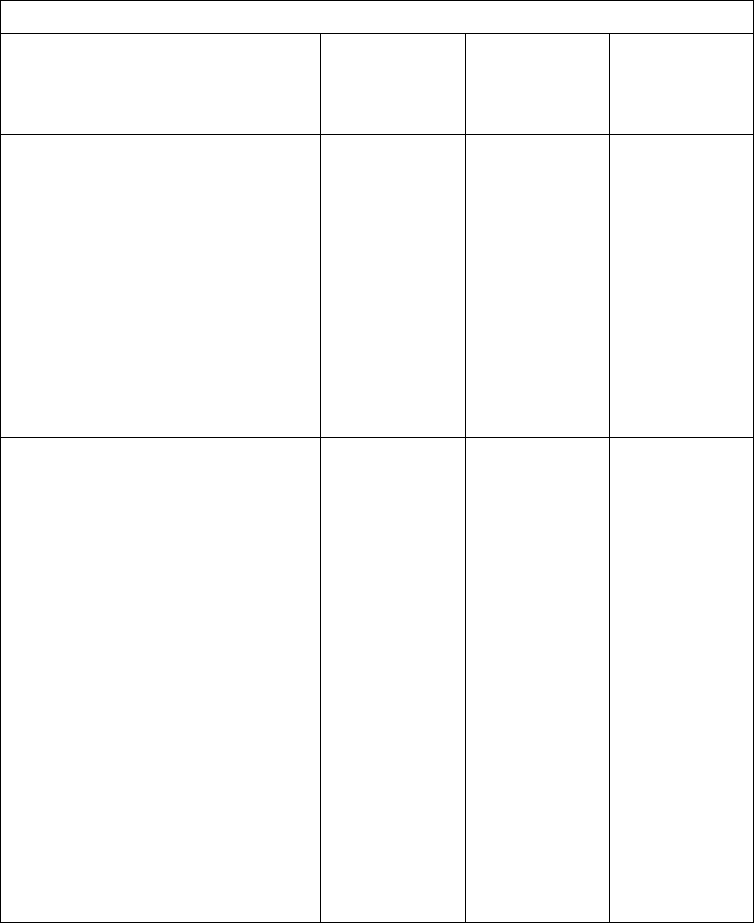
Table 19 on page 292 shows the valid entries for positions 28, 34, and 35 of the
file description specification for the various file types and processing methods. The
subsequent text describes each method of processing.
Table 19. Processing Methods for DISK Files
Processing Method Limits
Processing
(Pos. 28)
Record
Address
Type
(Pos. 34)
File
Organization
(Pos. 35)
Externally Described Files
With Keys
Sequentially
Randomly
Sequential within limits
(by record-address file)
Without Keys
Randomly/consecutively
Blank
Blank
L
Blank
K
K
K
Blank
Blank
Blank
Blank
Blank
Program Described Files
With Keys (indexed file)
Sequentially
Randomly
Sequential within limits
(by record-address file)
Without Keys
Randomly/consecutively
By record-address file
As record-address file
(relative record numbers)
As record-address limits file
Blank
Blank
L
Blank
Blank
Blank
Blank
A, D, G, P,
T, Z, or F
A, D, G, P,
T, Z, or F
A, D, G, P,
T, Z, or F
Blank
Blank
Blank
A, D, G, P,
T, Z, F, or
Blank
I
I
I
Blank
Blank
T
Blank
Consecutive Processing
During consecutive processing, records are read in the order they appear in the file.
For output and input files that do not use random functions (such as SETLL,
SETGT, CHAIN, or ADD), the ILE RPG compiler defaults to or operates as though
SEQONLY(*YES) had been specified on the CL command OVRDBF (Override with
Database File). (The ILE RPG compiler does not operate as though
SEQONLY(*YES) had been specified for update files.) SEQONLY(*YES) allows
multiple records to be placed in internal data management buffers; the records are
then passed to the ILE RPG compiler one at a time on input.
292 ILE RPG for AS/400 Programmer's Guide
