EncrypTight Deployment Planning
36 EncrypTight User Guide
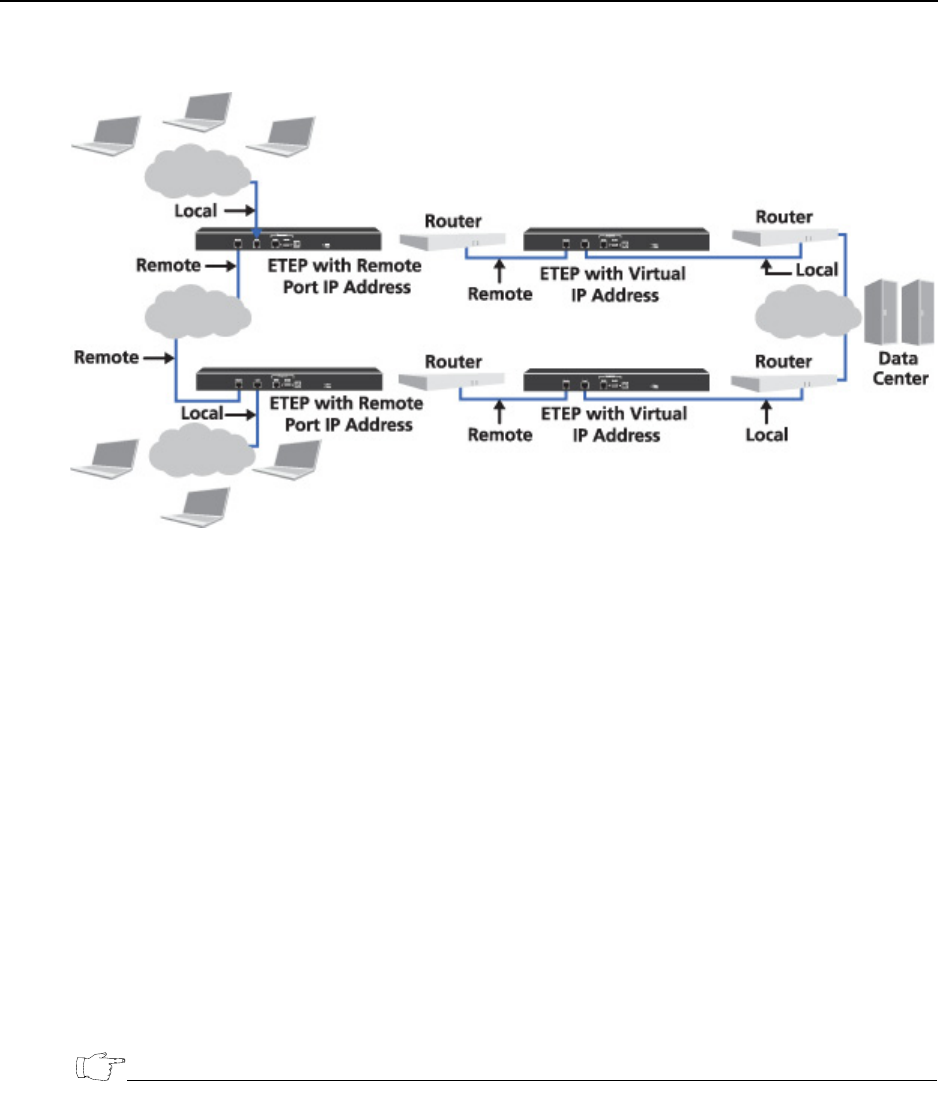
Figure 14 Using remote IP and virtual IP addresses to obscure the source address of
the original packet
ETEP PEPs operate in transparent mode by default and no IP address is assigned to the local or remote
ports. To use a remote port IP address or a virtual IP address, you need to disable transparent mode and
assign the needed IP addresses when you add and configure the ETEP in ETEMS. With a virtual IP
address, you also need to change the routing tables in the routers.
To use a virtual IP address as the source IP address:
1 Use ETEMS to disable transparent mode for the ETEP PEPs and configure the IP address settings for
the local and remote ports.
2 Make sure the ETEP PEPs are configured to use Layer 3 encryption policies.
3 Use ETPM to configure the network sets to use virtual IP addresses. For information about creating
network sets, see “Managing Network Sets” on page 167.
4 Use the policy editor in ETPM to disable both of the Addressing Mode Override options in order to
prevent the policy settings from overriding the virtual IP address settings. For more information about
policy settings, see “Policy Concepts” on page 181.
5 Verify that the WAN can direct the return traffic, destined for the virtual IP address, to the PEP’s
remote port. A static route entry and a static ARP entry will need to be configured in the WAN router.
For information on how to set up static routes, see the documentation for your router.
NOTE
Multicast network policies always preserve the network addressing of the protected networks.
Related topics:
● “Adding a Network Set” on page 170
● “Addressing Mode” on page 185
● “ETEP Configuration” on page 299


















