95
IP Addresses Section 5-1
5-1-3 Ethernet Unit IP Address Settings
An IP address must be set even for the Ethernet Unit before Ethernet commu-
nications can proceed. Either use the default for the Ethernet Unit's IP
address, or else use a Peripheral Device to set it in the DM Area words allo-
cated to the Unit as a CPU Bus Unit or in the CPU Bus Unit System Setup.
For details, refer to 2-7 Unit Setup Procedure.
5-1-4 Subnet Masks
Operation and management of a network can become very difficult if too
many nodes are connected on a single network. In such a case it can be help-
ful to configure the system so that a single network is divided up into several
subnetworks. This can be done by using part of the host number as a subnet
number. Internally the network can be treated as a number of subnetworks,
but from the outside it acts as a single network and uses only a single Net-
work ID.
To establish subnetworks, the Host ID in the IP address is divided into a Sub-
net ID and a Host ID by using a setting called the Subnet Mask. The Subnet
Mask indicates which part of the Host ID is to be used as the Subnet ID. All
bits in the Subnet Mask that correspond to the bits in the IP address used
either as the Network ID or Subnet ID are set to “1,” and the remaining bits,
which correspond to the bits in the IP address actually used for the Host ID,
are set to “0.”
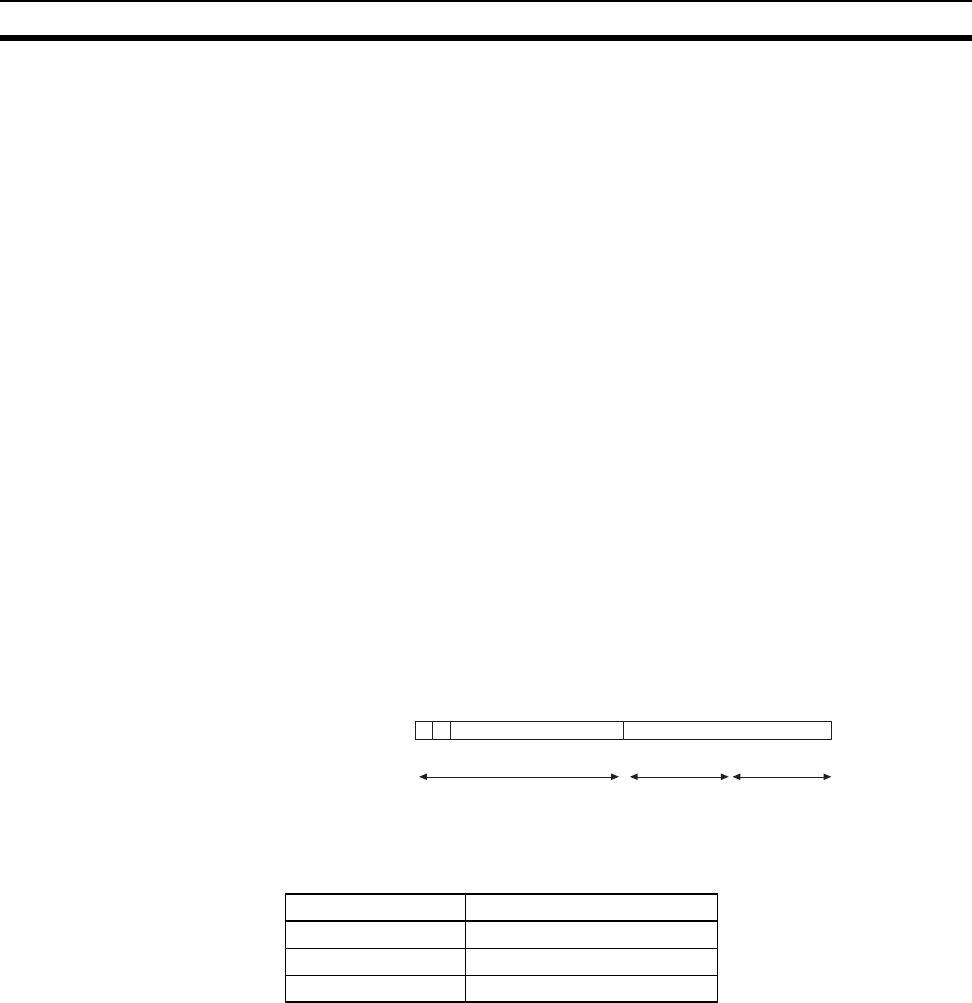
The following example shows the Subnet Mask for an 8-bit Subnet ID used in
a class-B IP address.
Set the same Subnet Mask value for all of the nodes on that subnetwork. If no
subnetworks are used, there is no need to set Subnet Masks. In that case, the
following Subnet Mask values will be used depending on the IP address class.
Class Subnet Mask value
Class A 255.0.0.0
Class B 255.255.0.0
Class C 255.255.255.0
Bit 31 15 0
Class B 1 0
Subnet mask 1111111111111111 1111111100000000 = FF FF FF 00
Network ID (14 bits)
Host ID (16 bits)
Network number
Subnet number Host number
