14 Chiller System Design and Control SYS-APM001-EN
Primary System Components
water entering and leaving the cooling tower is the range. The temperature
difference between the leaving water temperature and the entering wet-bulb
temperature is the approach.
Effect of load on cooling tower performance
As the building load—or heat rejection—decreases, range and approach also
decrease. This means that when the building is at part load, the cooling tower
can provide colder water at the same ambient wet-bulb temperature.
Effect of ambient conditions on cooling tower performance
As ambient wet-bulb temperature drops, the approach—at a constant load—
increases. This is counter-intuitive to many, and it must be considered when
cooling-tower-control strategies are developed. Detailed descriptions of these
conditions appear in “Chiller–tower energy balance” on page 91. For
additional information, refer to 2008 ASHRAE HVAC Systems and Equipment
Handbook, chapter 39, “Cooling Towers.”
3
Condenser-water pumping arrangements
Water-cooled chillers require condenser-water-system variations to be
considered. For a discussion of condenser-water temperatures and flow
rates, refer to “System Design Options” on page 27. Since air-cooled-chiller
condenser controls are part of the chiller design, they are not discussed in
this manual.
Most important, the inlet to the pump must have sufficient net positive head.
This often means locating the pump below the cooling-tower sump.
Single tower per chiller
In some applications each chiller has a dedicated cooling tower. This is most
likely to occur when chillers, and their accompanying towers, are purchased
at different times during the facility’s life—such as when additions are made.
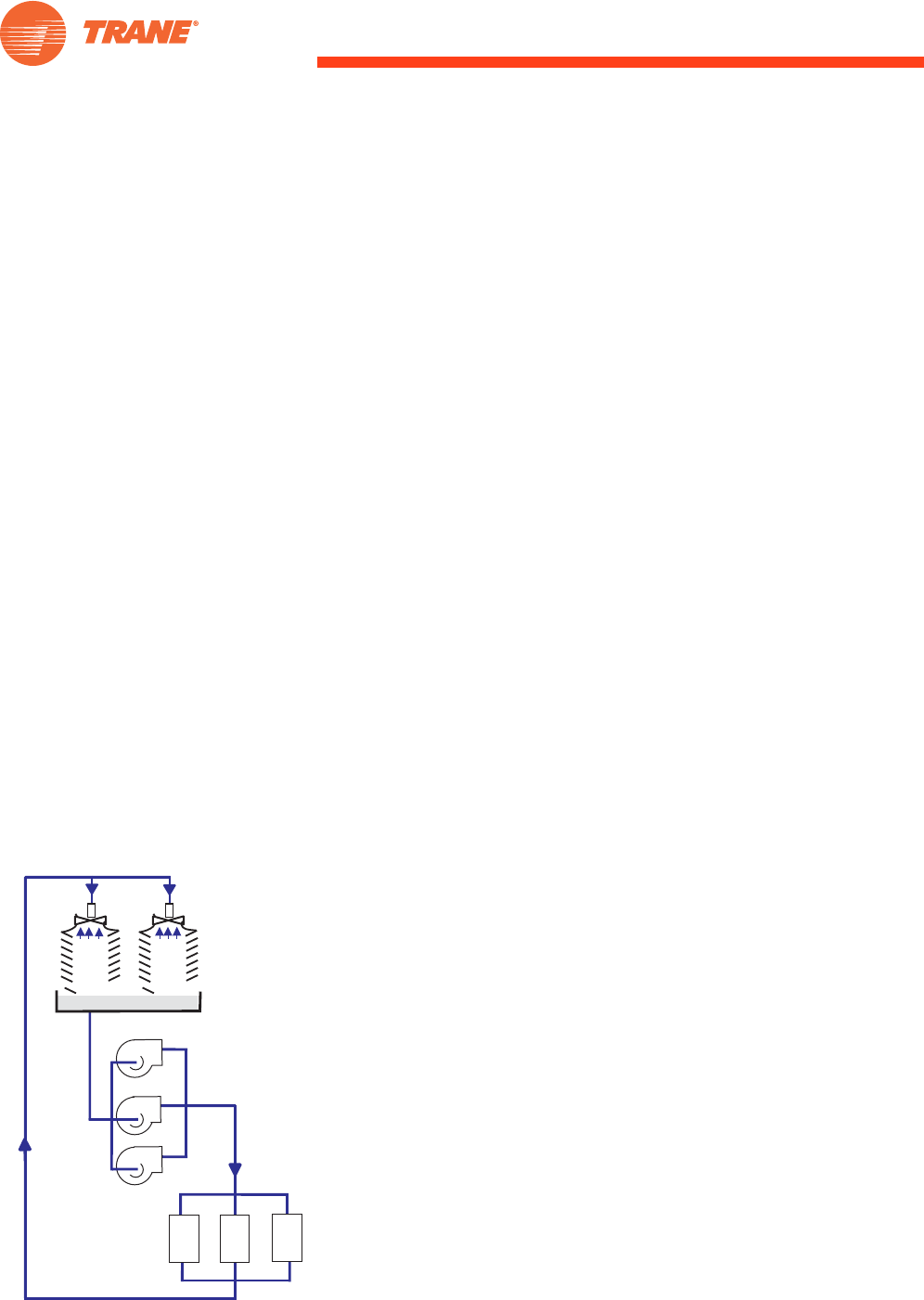
Manifolded pumps
A much-used pumping arrangement has a single cooling-tower sump with
manifolded pumps, one condenser water line, and separate, smaller, pipes
for each chiller as shown in Figure 15. This provides a number of advantages:
• Pumping redundancy
• If cooling towers cells can be isolated, any cooling-tower cell can run with
any chiller.
• Hydraulics are generally less problematic than on the chilled-water side.
• Cooling towers can be located remotely from chillers, with only a single
supply and return pipe to connect them.
Cooling
Towers
Manifolded
Pumps
Chillers
Figure 15. Manifolded condenser-
water pumps