Chilled-Water System Variations
SYS-APM001-EN Chiller System Design and Control 71
load. The details of operation are discussed in “Sidestream plate-and-frame
heat exchanger” on page 74.
Plate-and-frame heat exchangers isolate the building loop from the water in
the open cooling tower loop, but they must be cleaned, typically annually.
The labor and parts for cleaning and reassembly (e.g., gasketing) is an
expense that should be factored into the life-cycle cost of this option.
Refrigerant migration
Another method of “free” cooling is to transfer heat between the cooling
tower water and the chilled water inside a centrifugal chiller through the use
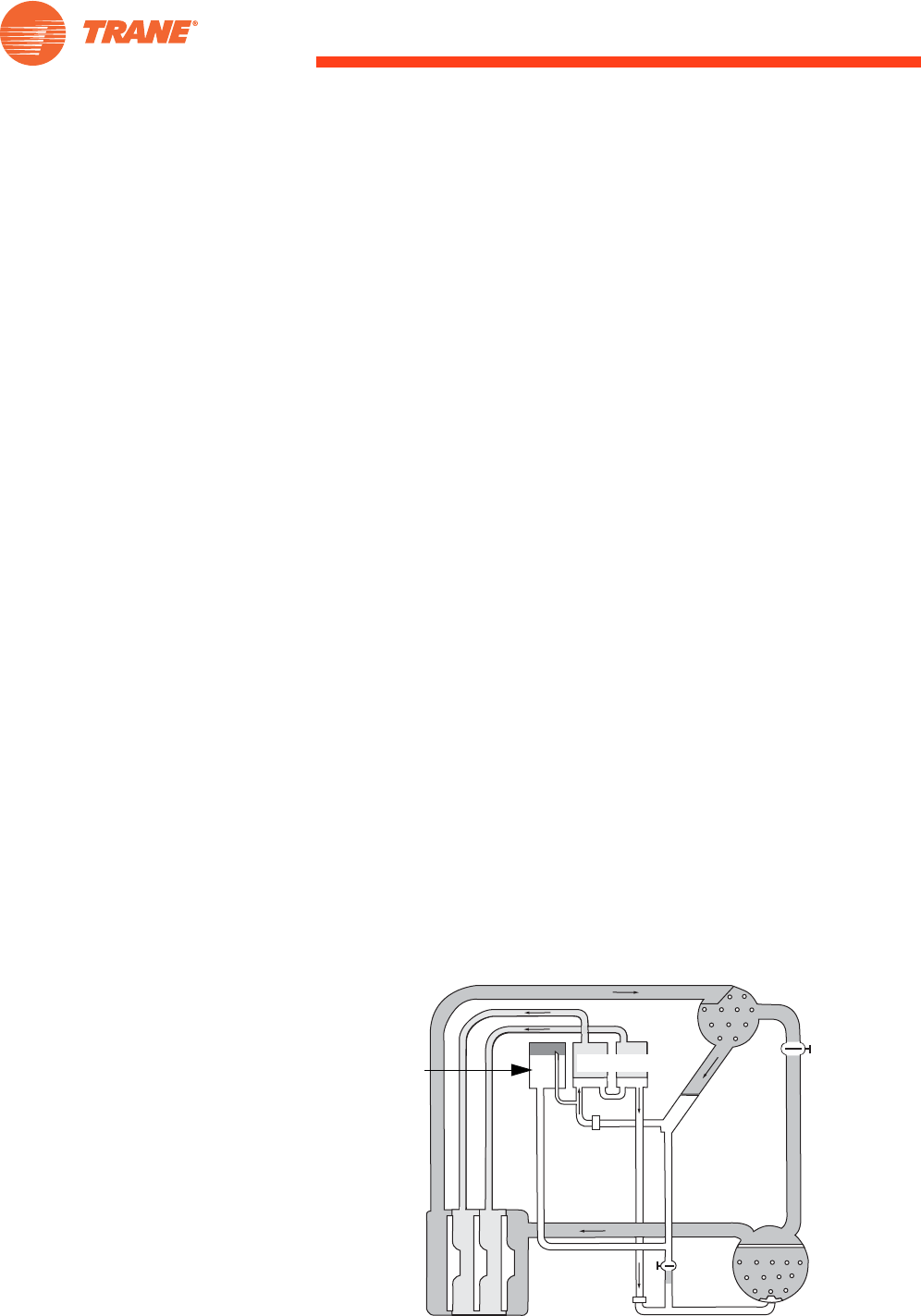
of refrigerant migration, also known as a thermosiphon. Figure 41 shows a
centrifugal chiller equipped for refrigerant migration free cooling. When the
temperature of the water from the cooling tower is colder than the desired
chilled-water temperature, the compressor is turned off and automatic shut-
off valves inside the chiller refrigerant circuit are opened, as shown in
Figure 42. Because refrigerant vapor migrates to the area with the lowest
temperature (and pressure), refrigerant boils in the evaporator and the vapor
migrates to the cooler condenser. After the refrigerant condenses, it flows by
gravity back through a shutoff valve to the evaporator. This allows refrigerant
to circulate between the evaporator and condenser without the need to
operate the compressor.
Depending on the application, it is possible for refrigerant migration in a
centrifugal chiller to satisfy many hours of cooling load without operating the
compressor. Free cooling chillers serving systems that can tolerate warmer
chilled-water temperatures at part-load conditions can produce more than 60
percent of the rated capacity without compressor operation. There are no
cooling coil fouling concerns because the cooling-tower water flows through
the chiller condenser and is separate from the chilled-water loop. There is no
additional expense for cleaning, as the condenser tubes are the same as
those used for normal cooling mode and should already be on a
maintenance schedule. In addition, fewer pipes, pumps, and fittings are
required, and no additional heat exchanger is required.
Figure 41. Refrigerant migration chiller in compression cooling mode
Compressor
Evaporator
Conditioner
Economizers
Refrigerant
Storage Tank