68 Chiller System Design and Control SYS-APM001-EN
System Configurations
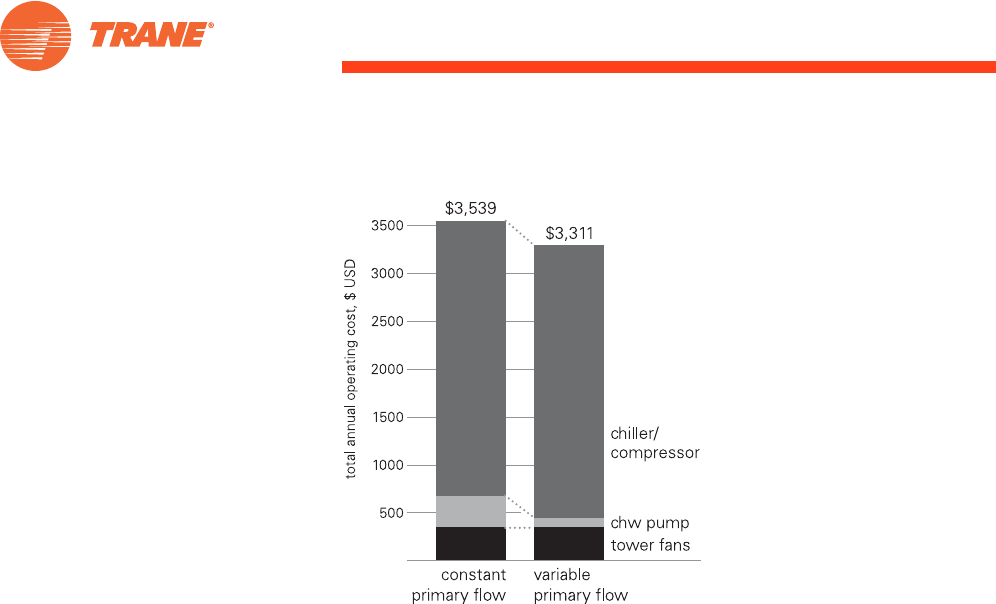
Figure 39. Example of operating-cost savings for a VPF, single-chiller plant
Analysis results are based on a 50-ton scroll chiller and a 5-hp chilled water pump for two-story office building
in St. Louis, Missouri.
Moderate “low T syndrome” by manifolding the chilled water pumps
Manifolding two or more chilled water pumps (or slightly oversizing a single
pump) can provide an individual chiller with more than its design chilled
water flow… which means that you can fully load the chiller even if the return
water temperature is colder than design.
Sometimes described as “overpumping,” this strategy does not cure “low T
syndrome”; it merely reduces the adverse effect of low T on system
operation.
29
(Refer to “Low T syndrome” on page 79). An example of low
T syndrome is receiving a depressed (for example, 49°F [9.4°C]) return-
water temperature rather than the design (for example, 56°F [13.3°C]) return-
water temperature.
Again, the only methods to load the chiller are to decrease the chilled-water
leaving temperature or to increase the flow. If the pumping power and speed
allows, the operator may be able to increase the chiller’s flow rate and
capacity. Do not exceed the pump’s operating envelope.
Guidelines for a successful VPF system
Chiller selection
• Select for the lowest possible minimum evaporator-flow limit (no more
than 40–60 percent of system flow)
• Select for the greatest tolerance to large flow-rate changes, while
maintaining required temperature setpoint
• Select chillers with approximately equal pressure drops across the
evaporator at the design flow rate