76 Chiller System Design and Control SYS-APM001-EN
Chilled-Water System Variations
Sidestream system control
The flexibility of sidestream applications is increased by the fact that the
devices are used to pre-cool return water, not to produce the system chilled-
water temperature. This means that they may be loaded by a different signal.
In the case of a plate-and-frame heat exchanger, as long as return water is
being cooled, there is an advantage to using it. A heat-recovery chiller can be
loaded to produce just the amount of hot water necessary using the
condenser-water leaving temperature as a signal. If preferential loading is
used with an absorption chiller, it may be loaded simply by decreasing its
leaving-water temperature.
Sidestream configurations may also be used to preferentially load chillers or
a heat exchanger used in a variable-primary-flow system, or to isolate chillers
that are incapable of the same flow variations as the rest of the system.
Preferential loading – series arrangement
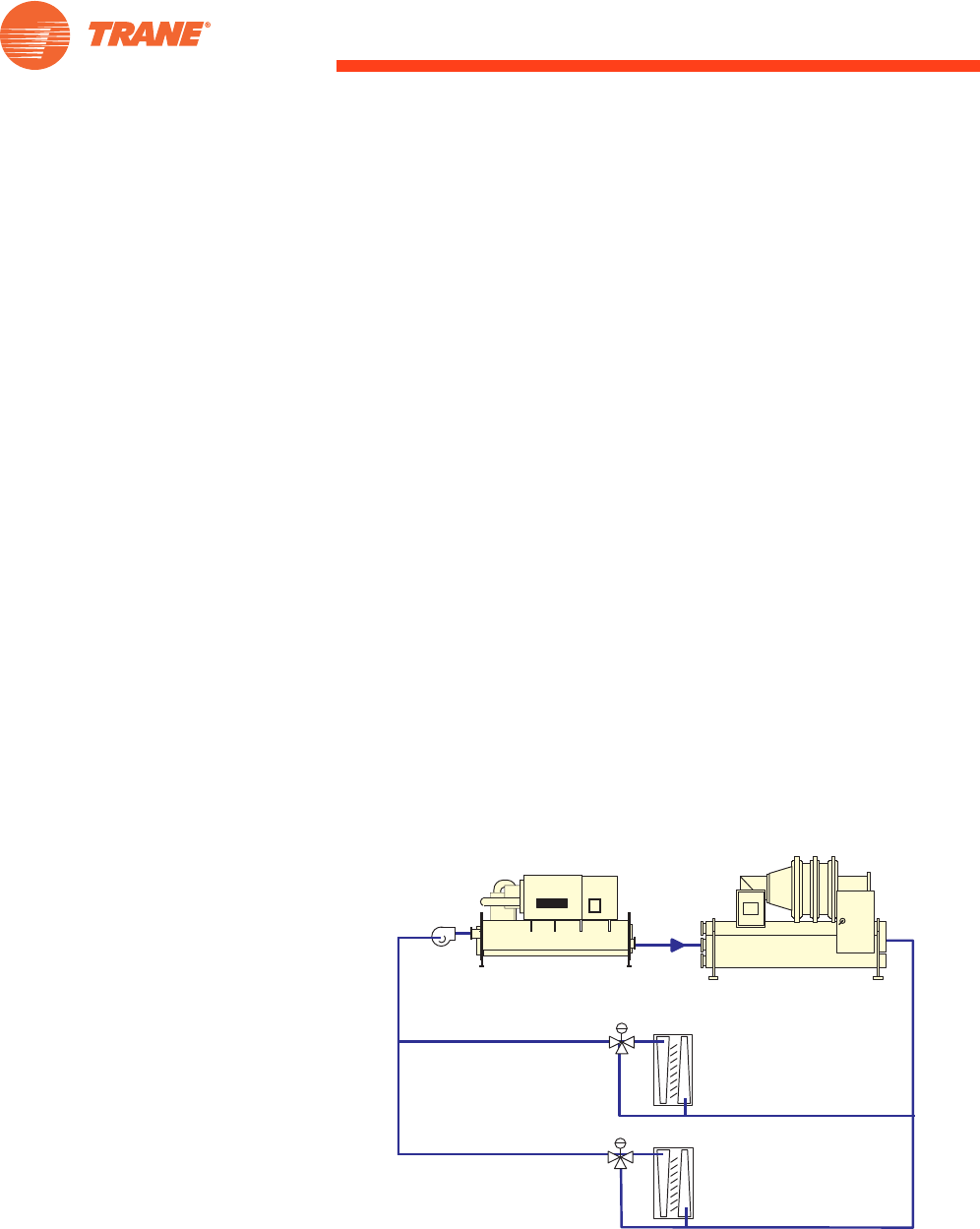
As previously discussed in “Series Chillers” on page 44, preferential loading
is very simple when chillers are placed in series. If both the upstream and
downstream chillers are given the system leaving water temperature
setpoint, the upstream chiller is preferentially loaded and the downstream
chiller operates whenever the upstream chiller can no longer achieve
setpoint. If the downstream chiller is given the system setpoint, and the
upstream chiller is given a warmer setpoint, then the downstream chiller
loads first. Another method for preferential loading uses compressor RLA to
determine when to bring on the next chiller.
Figure 47. Preferential loading - series arrangement
Chiller 2
setpoint = 42°F [5.5°C]
Chiller 1
setpoint = 42°F [5.5°C]
56°F [13.3°C]
Loads
49°F [9.4°C]
42°F [5.5°C]