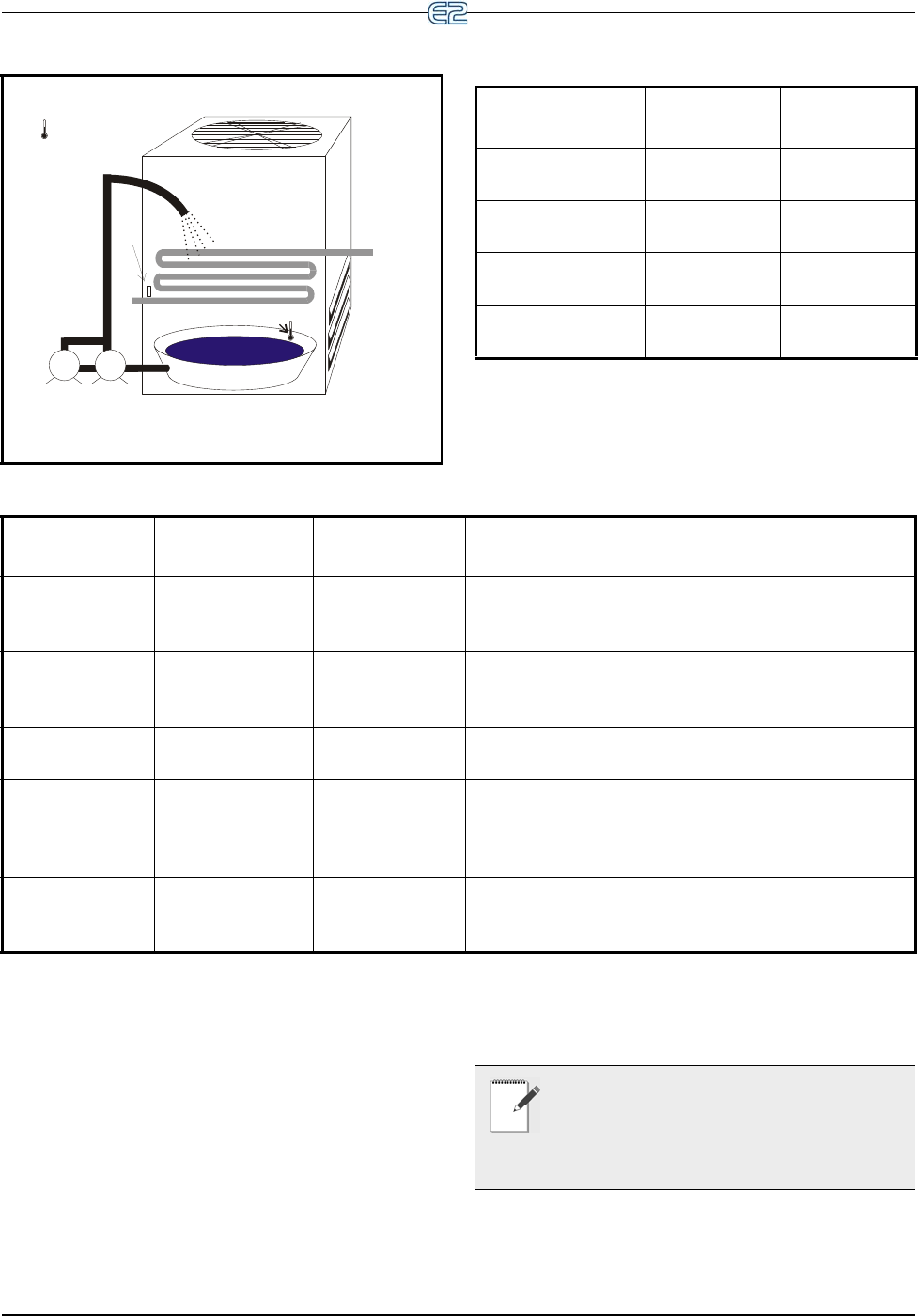
Figure 11-3 - Evaporative Condenser Diagram
EVAPORATIVE
CONDENSER
PUMP 2PUMP 1
WATER
SPRAY
FAN
INLET
OUTLET
DAMPERS
DISCHARGE
PRESSURE
COIL
WATER SUMP
TEMPERATURE
26509038
AMBIENT
TEMP
W
A
T
E
R
S
U
M
P
Table 11-3 - Suction Group Inputs
Input Sensor Type
Wiring
Instructions
Discharge Pressure 500 lb. Eclipse
transducer
see Table 9-1
on page 9-3
Ambient Temp Temperature see Table 9-1
on page 9-3
Water Sump Temp
(
Evap. only)
Temperature
(Immersion)
see Table 9-1
on page 9-3
Override Temp Sen-
sors (Evap. only)
Temperature
(Pip
e-Mount)
see Table 9-1
on page 9-3
Table 11-4 - Suct
ion Group Outputs
Output Device
Wire Output Board
Cont
acts to:
Set Fail-safe Dip
Switch to:
Notes
Condenser Fan
(Single-Speed)
N.C. N.C. (up) To ensure condensing during network and power failure,
co
ndenser fans should all be configured normally closed
(N.C.)
Condenser Fan
Relay (V
ariable-
Speed)
N.C. N.C. (up) The fan should operate at 100% during loss of communi-
cation with E2.
Dampers (Evap.
onl
y)
N.C. N.C. (up) Dampers should be open during communication loss
(N.C.).
Evaporator
Pu
mps (Evap.
only)
N.C. (see note) N.C. (see note) Some condensers have dual pumps that cycle at even
intervals. One pump should be wired N.C. and the other
N.O., so that only one pump runs during communication
loss.
Variable-Speed
F
an Output (to
inverter)
None (analog
point)
None (analog
point)
This 4AO or 8IO analog point sends the 0-100% fan
speed signal to the inverter.
Standard Circuits Software Overview • 11-5
11.3 Standard Circuits
Refrigerated cases that do not use case controllers are
controlled by Standard Circuit applications. In a Standard
Circuit application, the E2 is responsible for all case mon-
itoring and control; it uses the RS485 I/O Network to both
gath
er case temperature inputs and activate or deactivate
the liquid line solenoids, defrost modes, and fans. Also,
circuits that use ESR8s and MultiFlex ESRs are controlled
using Standard Circuits.
NOTE: Do not set up a Standard Circuit appli-
cation for a case that uses a CC-100 or CCB
case controller. These cases must use Case Cir-
cuit Control applications (see Section 11.4, Case Con-
trol Circuits).