FX
3G
/FX
3U
/FX
3UC
PLC User's Manual - Positioning Control Edition
Built-in Positioning Functions
8 1-Speed Positioning - DRVI/DRVA Instruction
8.1 Incremental Method and Absolute Method
B - 111
A
Common Items
B
Built-in
Positioning
Functions
Apx.
Example
Connection
8. 1-Speed Positioning - DRVI/DRVA Instruction
The built-in positioning function uses the drive to increment (DRVI) instruction or the drive to absolute (DRVA)
instruction to perform 1-speed positioning. Note that these two instructions use different target position
setting methods.
→ For important items common to all of the positioning instructions, refer to Section 4.7.
→ For example programs, refer to Chapter 12.
8.1 Incremental Method and Absolute Method
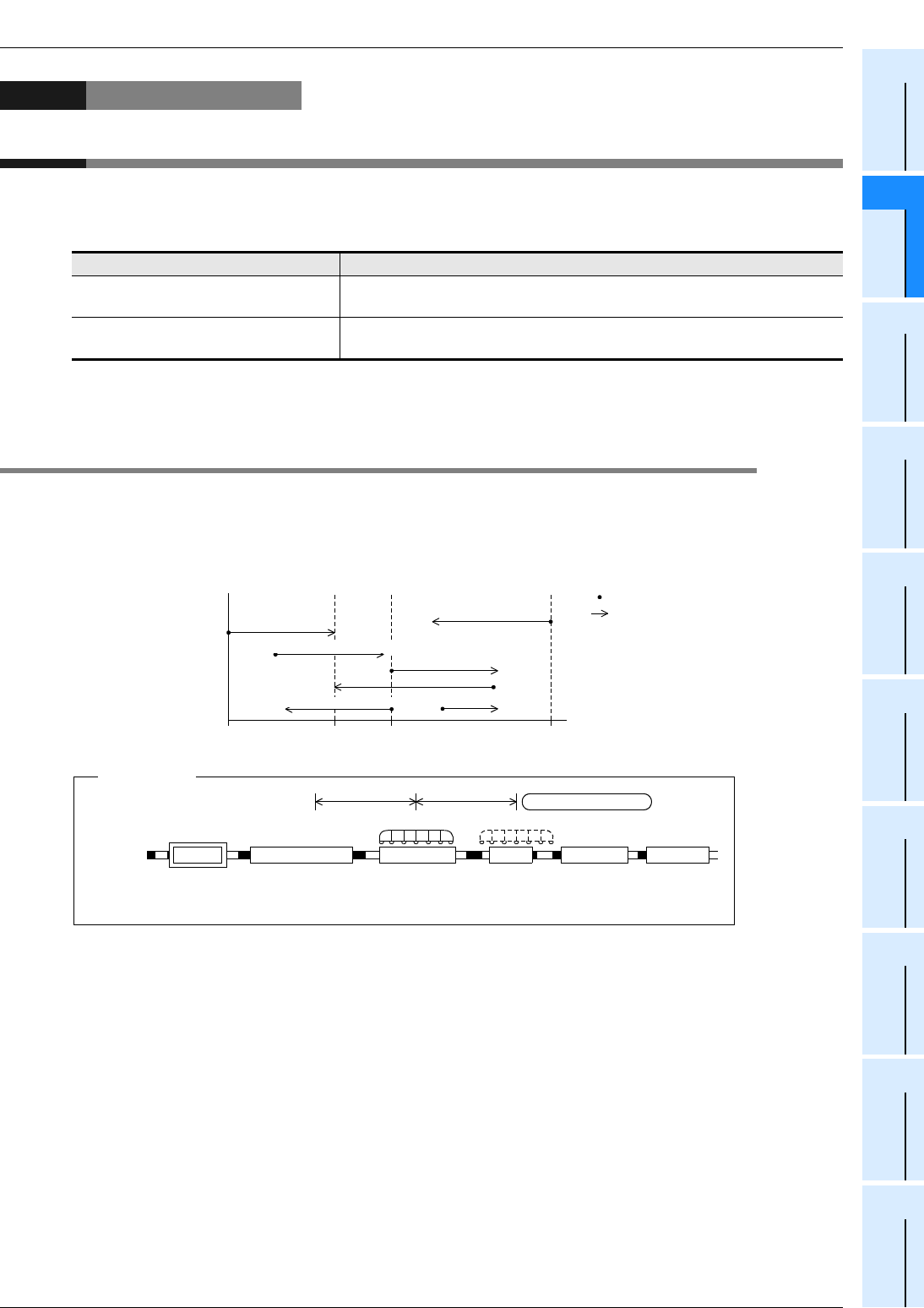
There are two target position setting methods for positioning operations as described below:
1. Incremental method (relative address setting method)
While regarding the current position as the start point, specify the transfer direction and the transfer distance
(relative address) to determine the target position.
Instruction Target position setting method
Drive to Increment (DRVI) instruction
Incremental method:
Uses a relative address to specify the target position.
Drive to Absolute (DRVA) instrument
Absolute method:
Uses an absolute address to specify the target position.
150
Point B
Transfer distance: -100
300
Point C
100
Point A
0
Origin
Start point
End point
To Ueno
Current position Target position
To go from Odawara (current position) to Atami (target position), set the distance (+20.7 km)
from Odawara to Atami.
Transfer distance: +50
Transfer distance: -150
Transfer distance: +100
Transfer distance: +100
Transfer
distance:
+100
Transfer distance:
-100
+20.7km-20.7km
Relative address
For example:
ShizuokaMishimaAtamiOdawaraShinyokohamaTokyo