Intel
®
IXP400 Software
Access-Layer Components: Time Sync (IxTimeSyncAcc) API
April 2005 IXP400 Software Version 2.0 Programmer’s Guide
284 Document Number: 252539, Revision: 007
20.2.1 IEEE 1588 PTP Protocol Overview
As mentioned at the beginning of this chapter, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is
used to synchronize independent clocks running in distributed network elements/nodes to a high
degree of accuracy (in the nanosecond to sub-microsecond range). This section provides a very
brief overview of the IEEE 1588 specification elements that relate to this IEEE 1588 hardware and
software subsystem. For a more complete understanding of IEEE 1588, refer to IEEE Std 1588 -
2002, IEEE Standard for a Precision Clock Synchronization Protocol for Networked Measurement
and Control Systems, November 8, 2002 (available at http://ieee1588.nist.gov/).
The PTP protocol defines four timing-related messages:
Sync, Delay_Req, Follow_Up and
Delay_Resp. Furthermore, the protocol identifies a network element/node as either a master or a
slave. The sequence and usage of the protocol messages vary depending on whether the node is
configured in slave or master mode. Components within the PTP messages, such as the UUID and
Sequence ID fields, are used by the master and slave elements/nodes to identify themselves and
relate the sequence in which the PTP messages are exchanged.
Synchronization Sequence
The master provides the clock source to which all the slave nodes synchronize.
The master sends a
Sync message to the slave node, carrying in it the master node’s system time as
a timestamp. The master may also use
Follow_Up message with the timestamp of the last Sync
message to provide more accurate timestamp details to a slave, after accounting for the PHY,
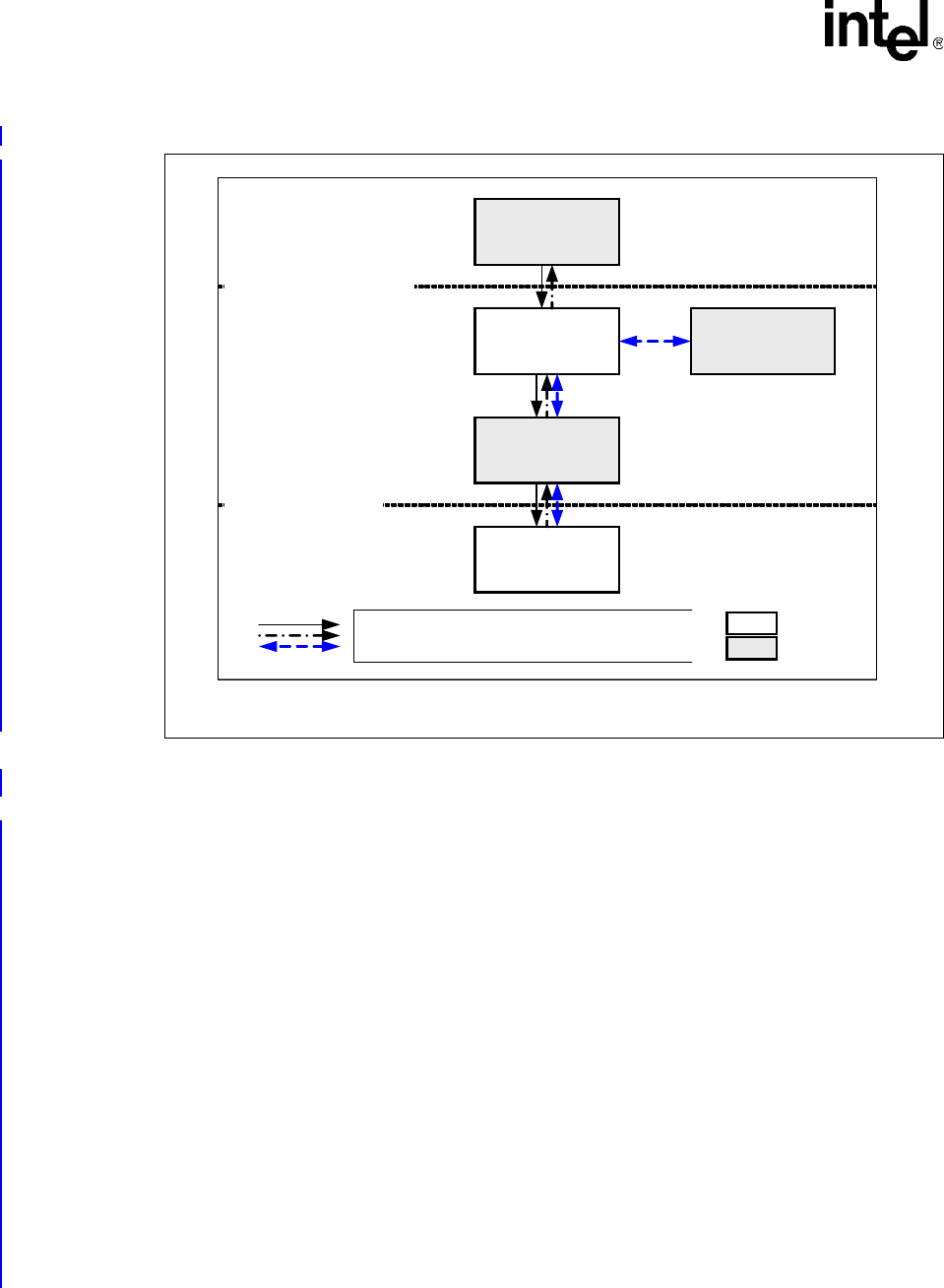
Figure 95. IxTimeSyncAcc Component Dependencies
B4392-01
Access-Layer Interface
Hardware Interface
Client Application
(1588 Protocol)
IxOSAL
IxTimeSyncAcc
IxFeatureCtrl
IEEE 1588
Black Solid Arrow - Client Invocation Path
Black Dotted Arrow - Interrupt Invocation Path
Blue Dotted Arrow - Interface with dependent components
Internal
External