Page 78 of
378
ITG Engineering Guidelines
553-3001-202 Standard 1.00 April 2000
Disable silence suppression at tandem nodes
Silence suppression introduces a different concept of half-duplex or
full-duplex at the voice message layer that results in a kind of statistical
multiplexing of voice messages over the WAN.
When Meridian 1 equipped with an ITG node serves as a tandem switch in a
network where some circuit-switched trunk facilities have an excessively low
audio level, silence suppression, if enabled, will degrade the quality of service
by causing choppiness of speech. Under tandem switching conditions with
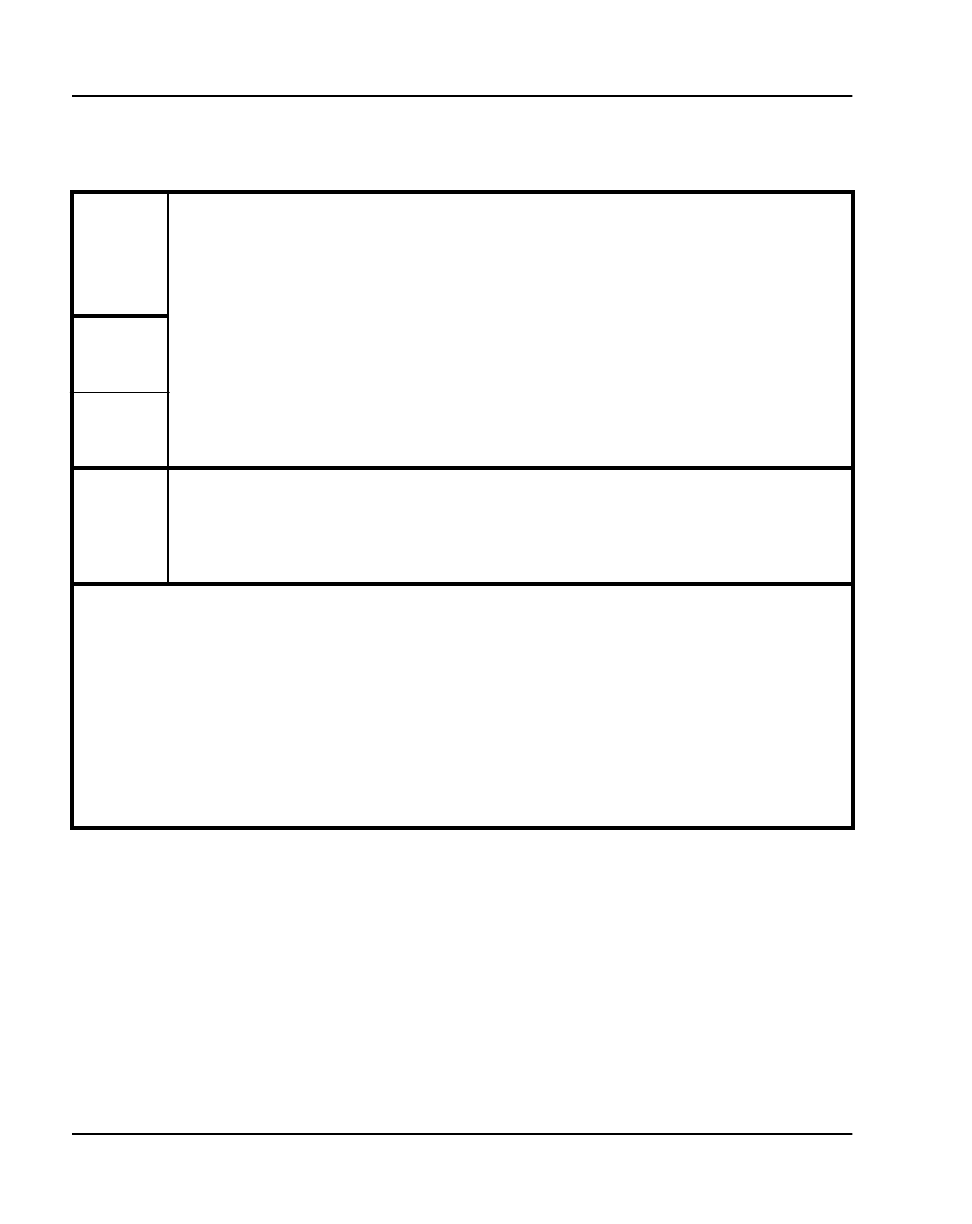
G.723.1
(5.3
kbit/s)
30 20 60 86 27.5 9.6 10.9 17.0
G723.1
(6.3
kbit/s)
30 24 64 90 28.8 10.2 11.5 17.0
T.30/T38
G3 Fax
Modem
(14.4
kbit/s)
16.6 30 70 96 46.1 33.6 37.5 50.9
25 30 70 96 30.7 22.4 25.0 33.9
Note 1:
Based on voice multiframe encapsulation for Realtime Transport Protocol per H.323 V2.
Note 2:
The bolded rows contain the default payload/packet size for each codec in the MAT.
Note 3:
T-LAN data rate is the effective Ethernet bandwidth consumption.
Note 4:
40% voice traffic reduction due to silence suppression; no suppression for fax.
Note 5:
T-LAN kbit/s for voice traffic = (1-40%)*2*Ethernet frame bits*8/frame duration in ms
Note 6:
WAN kbit/s for voice traffic = (1-40%)*IP packet bytes*8/frame duration in ms
Note 7:
24 ports per card for all codecs
Note 8:
Overhead (RTP/UDP header + IP header) of packets over the voice payload multiframe is 40
bytes; overhead of Ethernet frame over IP packet is 26 bytes.
Note 9:
The above bandwidth calculation does not include an Interframe gap, because of the low
probability of occurring in this type of application.
Table 5
Silence suppression enabled, T-LAN Ethernet and WAN IP bandwidth usage per ITG port
(Part 2 of 2)
Codec type
Codec
Multi -
frame
duration
in ms
(payload)
(one way)
Voice/fax
payload
Multi -
frame
in bytes
(one way)
IP voice
packet in
bytes
(one way)
Ethernet
voice
packet in
bytes
(one way)
Bandwidth
use on
T-LAN in
kbit/s
(two way)
Bandwidth
use on
WAN in
kbit/s
(one way)
WAN with
Frame
Relay
overhead
in kbit/s
(one-way)
WAN with
ATM
overhead
in kbit/s
(one-way)


















