General Description
Section 1
1-36
The attributes associated with surfaces, and the sections of this
manual where the information may be obtained, are listed below:
Attributes Related
Sections
Surfaces incidences - 5.13.3
Openings in surfaces - 5.13.3
Local coordinate system for surfaces - 1.6.3
Specifying sections for stress/force output - 5.13.3
Property for surfaces - 5.21.2
Material constants - 5.26.3
Surface loading - 5.32.3.4
Stress/Force output printing - 5.42
Shear Wall Design - 3.8.2, 5.53
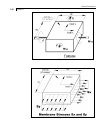
Local Coordinate system for surfaces
The origin and orientation of the local coordinate system of a
surface element depends on the order in which the boundary nodal
points are listed and position of the surface element in relation to
the global coordinate system
.
Let X, Y, and Z represent the local and GX, GY, and GZ the
global axis vectors, respectively. The following principles apply:
a. Origin of X-Y-Z is located at the first node specified.
b. Direction of Z may be established by the right hand
corkscrew rule, where the thumb indicates the positive Z
direction, and the fingers point along the circumference of
the element from the first to the last node listed.
c. X is a vector product of GY and Z (X = GY x Z). If GY and
Z are parallel, X is taken as a vector parallel to GX.
d. Finally, Y is a vector product of Z and X (Y = Z x X).