Line
Fuse
Blowing
1. If the line fuse blows with the (LINE) switch off, suspect either the input filter or the power
switch cable assembly.
2. If the line fuse blows when the spectrum analyzer is turned on, disconnect the power
cord and lift the drain of A6Q102 from TP108. If the line fuse still blows, suspect CR102
through CR105.
3. If the fuse does not burn out immediately, check
A6TP108
for a voltage of between
+215
V
and
+350
V.
4. If the voltage at TP108 is correct, disconnect the power cord. Wait 60 seconds for the high
voltage to discharge. Remove and check A6Q102.
5. If Q102 is shorted, Q103, Q104, CR108, U132 and
U207
may also be shorted.
6. The “Buck Regulator” procedure in the “Dead Power Supply” section can be used to check
the above components.
7. If
Q102
is working properly, measure the resistance between TP102 and
TPlOl
(positive
ohmmeter lead to TP102).
8. If the resistance is less than 1
kR,
suspect either
Q103
or Q104 in the DC-DC Converter.
Supply
Restarting
Every
1.5
Seconds
(Kick
Start)
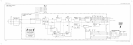
See function blocks G, D, I, and L of A6 power supply schematic diagram in the
component-level information binder. If there is a short on the power supply or on one of the
other assemblies, the power supply will attempt to “kick start.” (Every 1.5 seconds the supply
will attempt to start, but will be shut down by a fault condition.) The kick start and its bias
circuits provide power for the control circuitry during power-up. The kick start circuitry is an
RC oscillator which emits a 200 ms pulse every 1.5 seconds. These pulses switch current from
the input rectifier through
Q201
to charge C201. When the power supply is up, a winding on
T103 provides power to the control circuitry. This voltage is high enough to keep
Q201
turned
Off.
1. Monitor the waveforms at TP206 and TP208 simultaneously on an oscilloscope.
2. If the signal at TP208 goes high before the signal at TP206 goes low, an overcurrent
condition has been detected. Suspect a short in the secondary (output rectifier, voltage
regulators, or another assembly).
3. Do the first three steps of the “Buck Regulator” procedure of the “Dead Power Supply”
section to check the primary.
13-14 Display/Power Supply Section