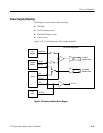
Theory of Operation
2715 Spectrum Analyzer Service Manual
3-89
At power up, there is a delay until R185 charges C290 to approximately 20 V, at
which time Q690 and Q691 turn on to supply power to the PWM IC. The capacitor
provides drive current until the PWM output (TP293) reaches 60 V relative to
special ground (TP190).
Initial pulses to the MOSFET switch are narrow, but they gradually widen as C691
(between pins 4 and 14 of the PWM IC) charges. If current through R260 at the
source terminal of the MOSFET switch exceeds 1.9 A, the pulse width is limited
until C163 at the primary center tap of the power transformer charges up to the
desired voltage. The PWM operates in a voltage control mode set by the string
R693, R682, R685, and R686, where the output voltage across C163 is compared
to the PWM’s internal +5 V reference. The negative end of the +5 V reference is
connected to TP293 (60 V above special ground). Frequency is set by C690 and
R694 in parallel with R681 and R680. Pin 10 of the PWM conducts through
CR680 and R672 to Q270 (a MOSFET switch) for fast positive transitions.
Transistor Q680 turns on for fast negative transitions. Series RC damping networks
R696/C692 and R684/C681 compensate the PWM transient response.
The MOSFET duty factor is approximately E
o
/E
in
. This will be approximately 16%
(2.2 s) at 250 V line input. The PWM IC has a maximum duty factor of 95%,
which means that voltage E
in
across storage capacitor C171 can drop to approxi-
mately 70 V before loss of regulation occurs.
Three components carry high current. These are MOSFET Q270, commutating
diode CR270, and coupled winding energy storage inductor (transformer) T190.
Capacitor C280 between the storage inductor windings compensates for leakage
inductance. The transformer has two auxiliary windings. One winding, pins 6 and
7, has a positive peak of 20 V and provides current for the PWM through 6.2 V
Zener diode VR690 and CR290. The other winding, pins 9 and 10, drives out of
phase current through a small capacitor connected to the chassis. This reduces line
conducted EMI by cancelling current flowing through stray capacitance to chassis
from the drain of Q270 and other parts connected to the same node.
Current into C163 at the center tap of the power transformer is continuous, as in a
Buck regulator. The current in the storage inductor ramps up when Q270 is on and
ramps down when CR270 conducts. Since there is current and stored charge in the
diode when Q270 turns on, L170 is included in the loop to limit current and reduce
power losses. Energy stored in L170 is recovered with three diodes and a capacitor
and transferred to the output.
Inverter. The inverter consists primarily of a PWM IC, a pair of MOSFETs, and the
power transformer. The MOSFETs are driven in push pull mode by U260, the
PWM IC. There is no regulation to modulate the pulse width of the drive signals.
Current flows through the power transformer from the center tap to the closed
MOSFET switch. The operating frequency is approximately 26 kHz as set by R664
and C661. Supply current for U260 is through R261 clamped to 12.4 V by
VR660 and VR661.