Appendix F: Miscellaneous
AWG2021 User Manual
FĆ17
maximum permitted frequency is called the Nyquist frequency and is 1/2 the
sampling rate.
If the signal has frequency components above the Nyquist frequency, they
appear on this limited discrete frequency axis too. They appear as no
different than noise aliased from the Nyquist frequency. For example, if there
is a signal 5 MHz above the Nyquist frequency, it appears as if it is 5 MHz
below the Nyquist frequency. On the other hand, in the D/A conversion, a
frequency component is output aliased above the Nyquist frequency.
To deal with aliasing, first it is necessary to sample with a clock greater than
double the highest frequency component in the signal. Second, a low-pass
filter is required to block any signal above the Nyquist frequency.
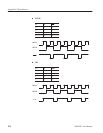
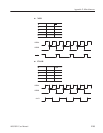
The frequency spectrum frequency range and resolution depend on the time axis
sampling rate and the record length (N).
For the given data length on the time axis, FFT has frequency components from
–N/2 to N/2–1. However, when the real number data on the time axis is
transformed, FFT gives results symmetrical about 0 Hz (DC). Because of this
symmetry, all the necessary frequency data is contained between 0 and N/2 – 1.
Thus, with FFT if values are given from zero to the positive N/2 point, this is
enough. Since the non-DC components have energy dispersed on both the
positive and negative sides, the DC component is 2x the other components.
Since the DC component is scaled by 1/2 with the FFT editor, DC and the other
components can be handled equally.
Since FFT has N/2 sampling points on the discrete frequency axis between DC
and the Nyquist frequency (F
N), the frequency resolution is FN/(N/2). Since the
Nyquist frequency is one half the sampling rate (f
s), the frequency resolution can
also be expressed as f
s/N.
Therefore, if the sampling rate is fixed, when the record length is increased, the
frequency resolution rises. On the other hand, if the record length is fixed,
raising the sampling rate raises the Nyquist frequency and lowers the frequency
resolution.
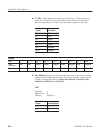
The phase is the quantitative displacement from the standard time. The cos(2 π
ft) has a 0 phase, but sin(2 π ft) has a 90 degree delay. The standard time is the
sampling start time.
Record Length and
Frequency Resolution
Relationship Between
Phase and Delay