DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 2 Configuring BGP IP VPN
2-16
Caution
The configured static private FTN and ILM take effect only after the
corresponding public LSP is set up. To set up the public LSP, refer to
Procedures for Configuring Basic MPLS. You can set up a public LSP
through LDP or static configurations.
2.3.2 Configuring an Inter-AS VPN
On an actual network, different sites of VPN users may be located on different ASs and mutual
communication is required between these sites. In this case, the VPN routes should be
exchanged between different ASs. This technology is called the inter-AS VPN.
RFC 4364 introduces three types of inter-AS VPN schemes:
OptionA: VRF-to-VRF mode
OptionB: single-hop MP-EBGP mode
OptionC: multi-hop MP-EBGP mode
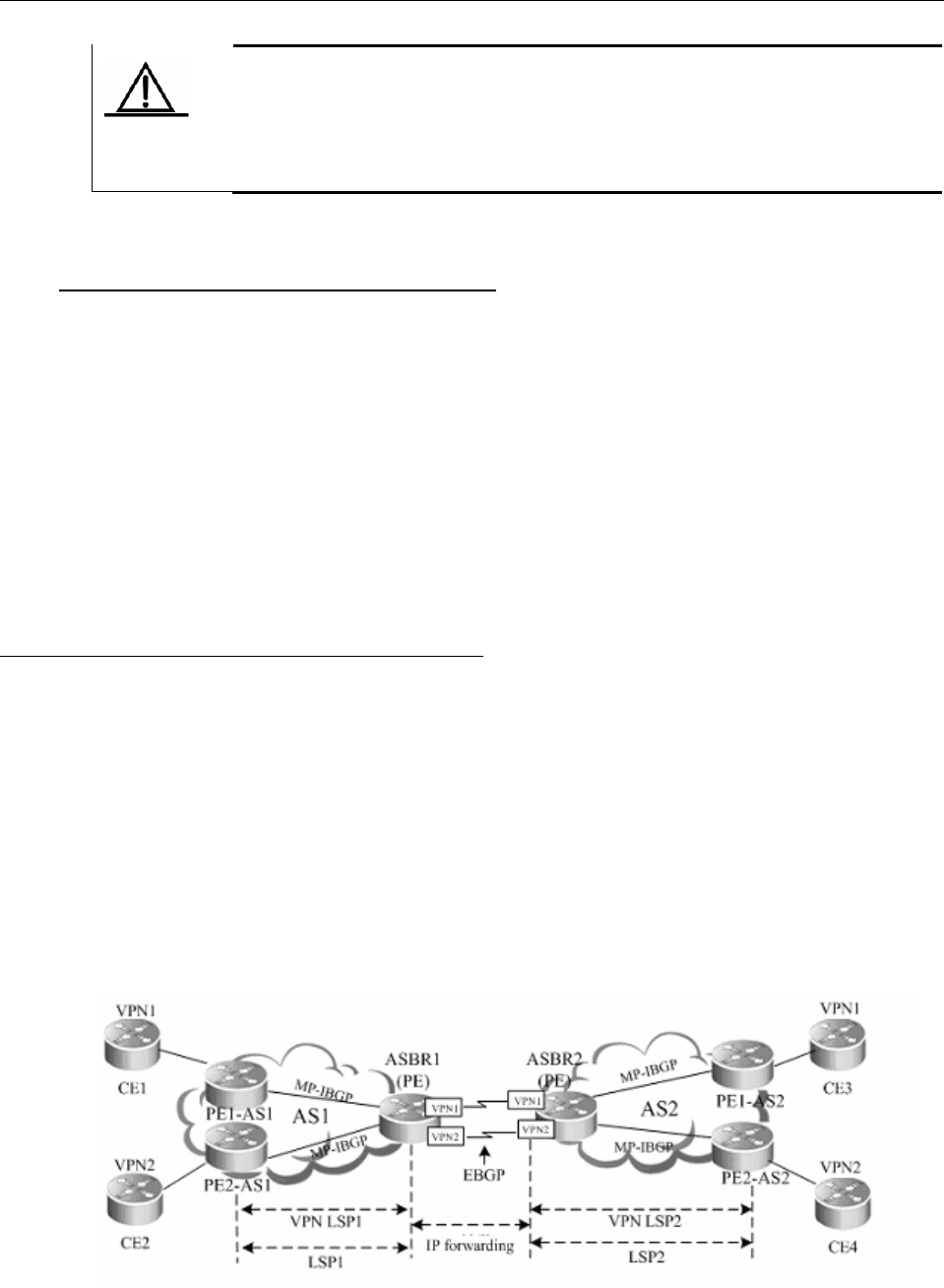
2.3.2.1 OptionA: VRF-to-VRF Mode
Also referred to as the VRF back-to-back, the VRF-to-VRF mode features easy implementation.
The ASBR of an AS sets up a VRF for each inter-AS VPN to bind the VRF to an interface. The
VRFs on ASBRs then exchange VPN routes through the interface.
The purpose to create a VRF and bind it to an interface is as follows:
Receive VPN routes from the local AS.
Set up an EBGP connection between the VRF and the VRF of another AS to exchange IPv4
routes.
Figure 8 VRF-to-VRF inter-AS VPN


















