DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 4 LACP Configuration
4-3
address is , the higher the system ID will be. The system with the higher system ID
determines the port state.
4.4.2 LACP Port ID
Each port owns an independent LACP port priority, which is configurable. The port
ID consists of LACP port priority and port number. First compare the two port
priorities: the lower the port priority value is, the higher the port ID is. Then compare
the two port numbers if the two port priorities are equal: the smaller the port number
is, the higher the port ID is.
4.4.3 LACP Master Port
When the dynamic member port is up, LACP selects a port with the highest priority
in the aggregation group based on the port rate, duplex rate, ect. Only can the ports
with the same attributes with the master port be aggregated and join in the packet
forwarding in the aggregation group. When the port attributes change, LACP
re-selects the master port without deaggregation. But when the new master port is
not aggregated, LACP deaggregates the member ports in the aggregation group
and re-aggregates.
4.4.4 LACP Negotiation Procedure
Upon receiving the LACP packets from the peer port, the system ID with higher
priority is selected. On the end of higher system ID, set the ports in the aggregation
group are to be aggregated in the descending order of port priority(when the number
of ports in the aggregation group exceeds the maximum port number, the state of
the ports exceeding the aggregation capacity is sups.) Upon receiving the updated
LACP packets on the peer port, the corresponding port is to be aggregated.
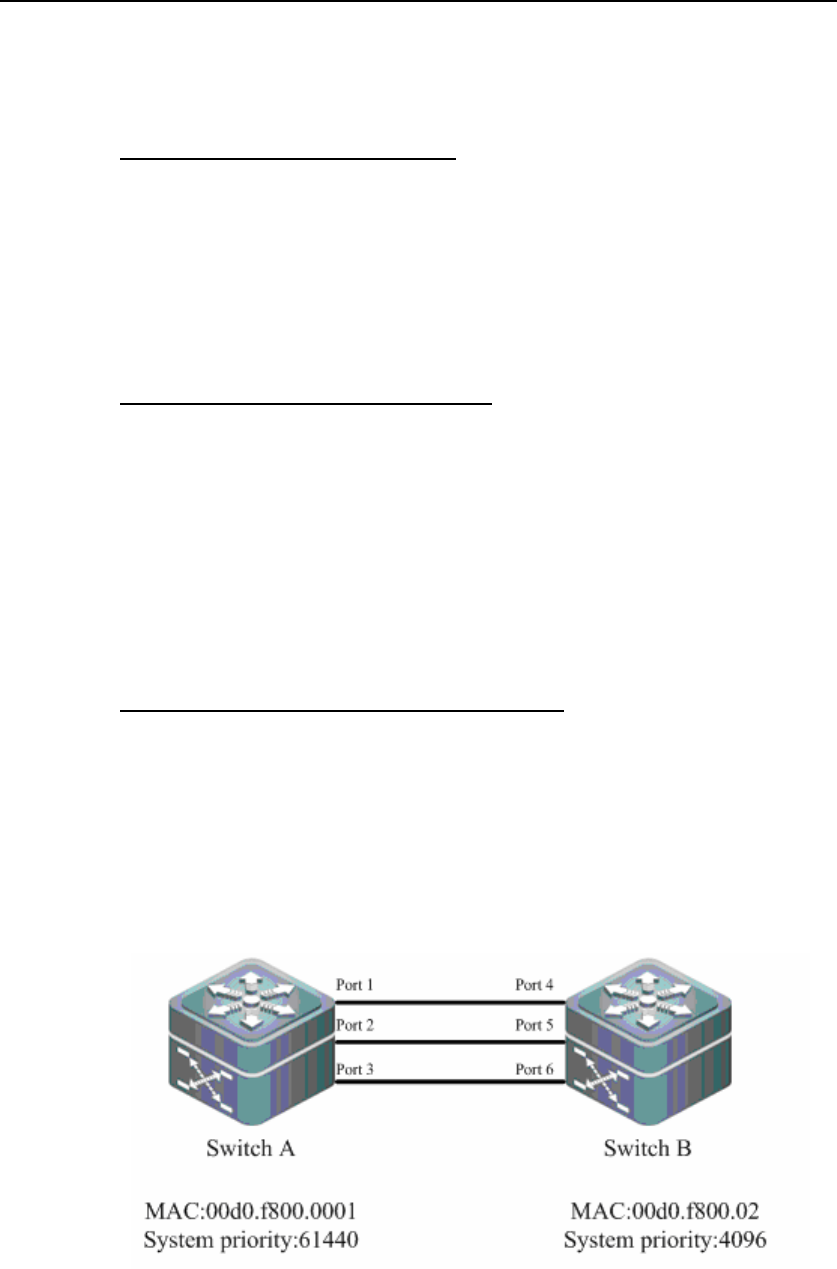
Figure-1 LACP Negotiation
As shown in Figure-1, switch A and switch B are interconnected through the 6 ports.
Set the system priority for the switchA and the switchB to be 61440 and 4096


















