DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 10 MSTP Configuration
10-3
four bits denote the priority, while the last twelve bits denote the system ID for
extending the protocol in the future. This value is 0 in the RSTP, so the priority
of the bridge should be configured as the multiple of 4096.
Priority value System ID
Bit 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Value
3276
8
1638
4
819
2
4096
204
8
102
4
51
2
25
6
12
8
6
4
3
2
1
6
8 4 2 1
10.1.1.4 Spanning-Tree Timers
The following describes three timers impacting the performance of spanning
tree.
z Hello timer: Interval to send the BUDU message.
z Forward-Delay timer: Interval to change the port status, that is, the time
interval at which the port switches from the listening status to the learning
status and vice versa when the RSTP protocol runs in the compatible STP
protocol mode.
z Max-Age timer: The longest time for the BPDU message. The system will
discard the message when the timer times out.
10.1.1.5 Port Roles and Status
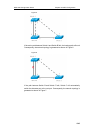
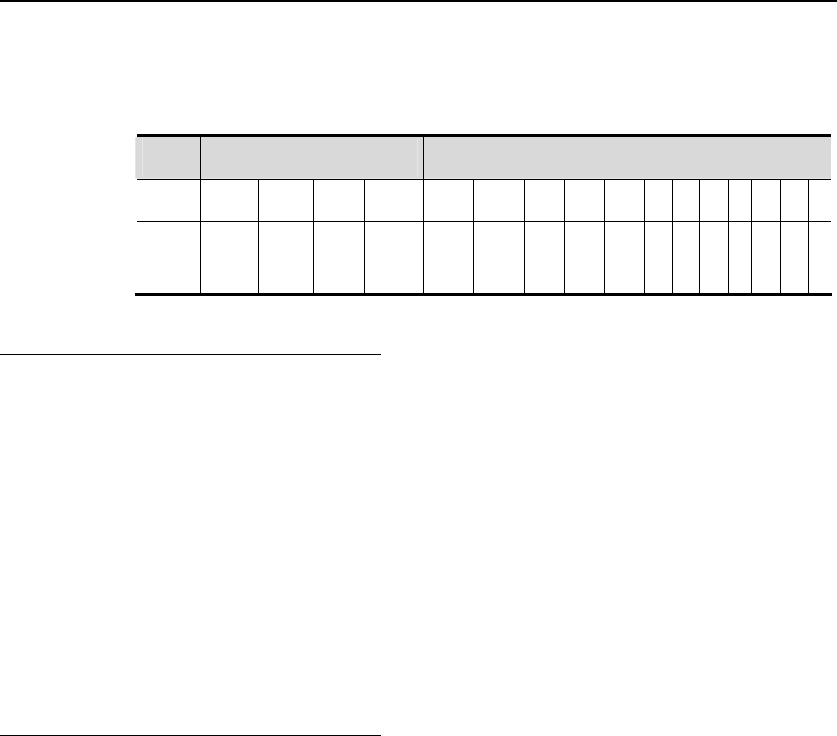
A port plays a role to present its function in the network topology.
z Root port: The port that provides the shortest path to the root bridge.
z Designated port: The port through which each LAN is connected to the root
bridge.
z Alternate port: The alternate port of the root port that will take up its work
when the root port fails.
z Backup port: The backup port of the designated port. If two ports of a
bridge are connected to a LAN, the port with higher priority is the
designated port and the other one is the backup port.
z Disable port: The port that is not in the active status, namely, the ports
whose operation status is down.
Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 below show the roles of various ports:
R = Root port D = Designated port A = Alternate port B = Backup port
Unless otherwise stated, the priorities of these ports are in the descending order
from left to right.