DES-7200 Configuration Guide Chapter 1 VRRP Configuration
1-2
device is in the normal working status. If the standby device within the group
doesn’t receive the message from the master device for a long time, it becomes
the master. If more than one device within the group become master, repeat the
preempt process in step 1.In this process, the device with the maximum priority
will be selected as the master router to execute the VRRP backup function.
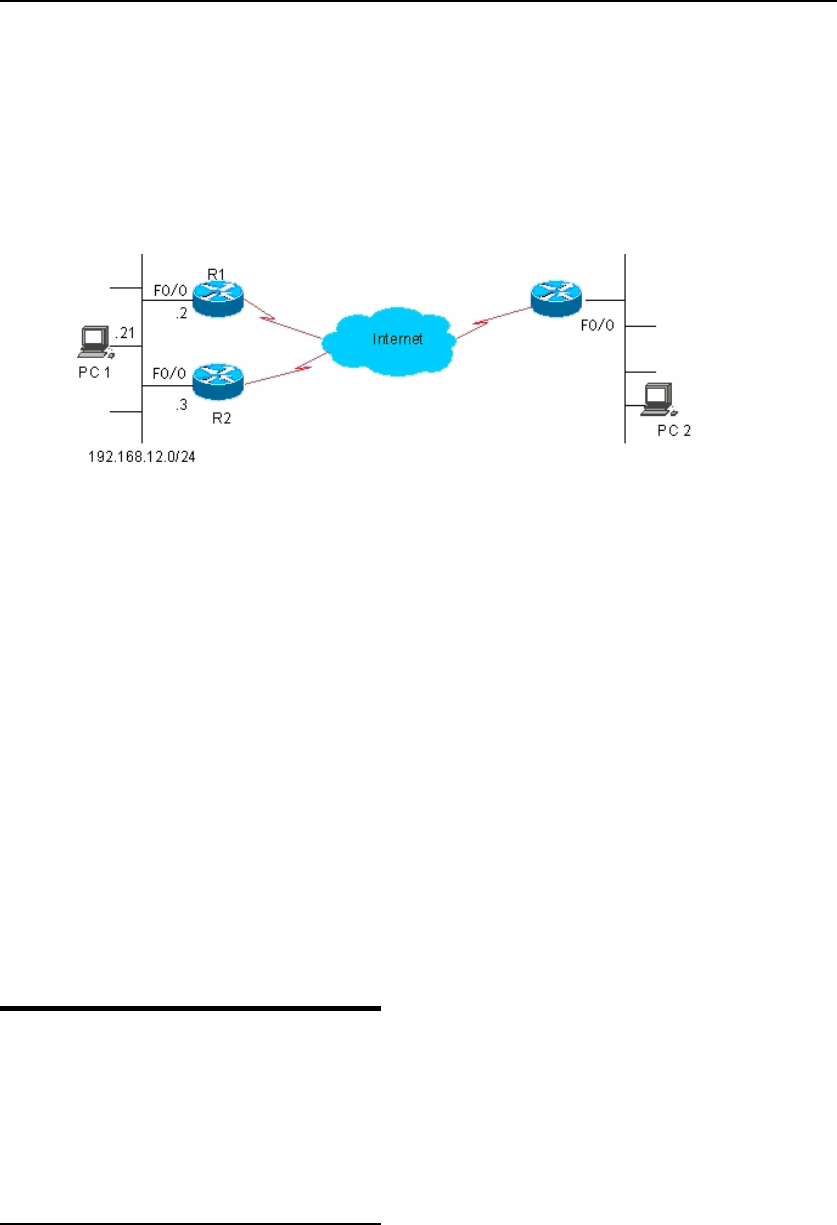
Figure-1: VRRP working principles
Once a master device is elected in a VRRP backup group, the hosts in the LAN will
execute route forwarding through that master device. The communication process is
illustrated in Figure-1.
As you can see, R1 and R2 are connected with LAN 192.168.12.0/24 through the
VRRP-enabled Ethernet interface Fa0/0. All hosts in the LAN use the IP address of the
virtual router of the VRRP group as the default gateway. The hosts in the LAN only
know the virtual router of the VRRP group, while the master router in the VRRP which
is implementing the forwarding function is transparent to them. For example, if host PC
1 in the LAN is communicating with host PC 2 in another network, PC 1 will use the
virtual router as the default gateway to send packets to PC 2. After receiving the
packets, the master router in the VRRP group forwards them to PC 2. In this
communication process, PC 1 only feels the virtual device but does not know whether
R1 or R2 works. The master router is elected between R1 and R2 in the VRRP group.
Once the master router fails, the other router automatically becomes the master.
1.2 VRRP Applications
There are two VRRP application modes: basic and advanced. In basic applications,
simple redundancy is implemented with a single backup group, while in advanced
applications multiple backup groups are used to implement both route redundancy and
load balancing.
1.2.1 Route Redundancy
The basic VRRP applications are illustrated in Figure-2.
Figure-2: Basic VRRP applications


















